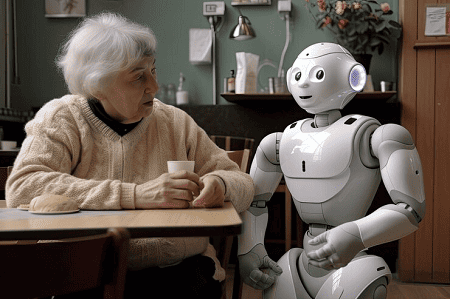
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is a rapidly evolving field focused on using robotic technologies to support aging populations, improve their quality of life, and assist caregivers. As the global elderly population continues to grow, robotics presents a promising solution to address challenges related to healthcare, mobility, and independence.
Here are some key areas where advanced robotics is making an impact in elderly care:
1. Assistive Robots
- Robotic Prosthetics: These robots assist elderly individuals with mobility issues by providing prosthetic limbs or exoskeletons that help them regain movement and independence.
- Robotic Wheelchairs and Walkers: Advanced wheelchairs and walkers are being equipped with sensors and AI to help elderly users navigate obstacles, avoid falls, and navigate through spaces autonomously.
2. Robotic Companions
- Social Robots: Robots like Paro (a therapeutic robot designed to look like a baby seal) offer companionship and emotional support, helping to reduce loneliness and improve mental well-being.
- Pet Robots: Non-living robotic pets can provide comfort, reduce feelings of isolation, and improve mental health without the responsibilities of caring for a real pet.
3. Healthcare and Monitoring
- Telepresence Robots: These robots allow healthcare providers to remotely monitor and interact with elderly patients. This reduces the need for frequent in-person visits while maintaining a high level of care.
- Health Monitoring Robots: Robots equipped with sensors can track vital signs (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure, temperature), detect falls, and alert caregivers or medical professionals in case of an emergency.
4. Robotic Caregivers
- Robots for Daily Tasks: Robots are being developed to assist with daily activities like dressing, feeding, cleaning, and even managing medications, helping elderly individuals live independently at home for longer.
- Humanoid Robots: These robots can provide physical help, such as lifting and transferring elderly individuals from beds or chairs, and can offer assistance with basic caregiving tasks.
5. Smart Home Integration
- Smart Devices: Advanced robots are being integrated with IoT (Internet of Things) technologies in smart homes to automate tasks like adjusting the temperature, controlling lights, and reminding elderly individuals to take medications.
- Fall Detection Systems: Sensors and robots working together can detect falls and immediately notify caregivers or emergency services.
6. AI and Machine Learning
- Personal Assistants: Robots powered by AI can assist elderly individuals in managing their daily routines, such as reminding them to take medicine or helping them make phone calls.
- Machine Learning: Over time, robots can learn the preferences and habits of elderly individuals, allowing them to offer more personalized care.
7. Rehabilitation and Therapy
- Robotic Physical Therapy: Robots designed for rehabilitation can help elderly individuals recover mobility and strength by guiding them through specific exercises or movements.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Robots: These technologies can be combined with robotics to provide elderly individuals with therapeutic exercises in a controlled, safe environment.
Benefits of Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care:
- Increased Independence: Many robots are designed to help elderly individuals maintain their independence and perform everyday tasks that would otherwise require assistance from a caregiver.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Robotic companions, healthcare monitoring, and entertainment robots can improve social engagement and reduce the emotional burden of aging.
- Reduced Caregiver Stress: Robots can lighten the workload of caregivers by handling repetitive tasks, offering monitoring, and providing emotional support to elderly individuals.
- 24/7 Assistance: Robots can be available around the clock, providing consistent care even when human caregivers are unavailable.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Cost: High-end robots and systems can be expensive, limiting their accessibility, especially for those with limited financial resources.
- Acceptance: Some elderly individuals may be hesitant or uncomfortable with robotic assistance due to unfamiliarity or fears about technology.
- Ethical Issues: The use of robots in elderly care raises questions about the replacement of human interaction, privacy concerns, and the long-term effects of robotic caregiving.
In conclusion, Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care offers a range of opportunities to improve the lives of elderly individuals and their caregivers. With continued advancements in robotics, AI, and machine learning, the potential for personalized, efficient, and empathetic care is vast, though careful consideration must be given to the challenges and ethical implications involved.
What is Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care refers to the use of cutting-edge robotic technologies designed to assist, support, and improve the quality of life for elderly individuals. As the global population ages, there is an increasing need for solutions that help older adults live independently, safely, and comfortably while reducing the burden on caregivers. Advanced robotics aims to address these challenges by providing personalized care, promoting social interaction, assisting with daily tasks, and ensuring the overall well-being of seniors.
Here are the main aspects of Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care:
1. Assistive Technologies
- Mobility Assistance: Robots like exoskeletons, smart wheelchairs, and robotic walkers help seniors who have mobility issues, enabling them to move independently and avoid falls.
- Prosthetics and Orthotics: Robotic prosthetic limbs or devices can assist those who have lost limbs, providing better movement and functionality.
2. Healthcare Support
- Monitoring Health: Advanced robots equipped with sensors can monitor an elderly person’s health, track vital signs (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels), and alert caregivers or medical professionals if something abnormal is detected.
- Telemedicine Robots: Robots enable remote consultations with doctors and specialists, allowing elderly individuals to receive care from the comfort of their homes.
3. Robotic Caregivers
- Personal Assistance: Robots can assist elderly individuals with daily tasks such as dressing, eating, cleaning, or taking medications. This allows seniors to maintain their independence while ensuring they get the help they need.
- Humanoid Robots: These robots are designed to resemble humans and can offer companionship, help with daily routines, and even perform basic caregiving tasks like lifting and transferring.
4. Social Interaction
- Companionship Robots: These robots can provide emotional support and social interaction, which can help reduce loneliness and improve mental well-being. Robots like Paro (a therapeutic robotic pet) or social robots with AI features offer comfort and engage in conversation.
- Entertainment: Some robots provide entertainment by playing music, showing videos, or engaging elderly individuals in games, helping to keep their minds active and engaged.
5. Safety and Security
- Fall Detection: Robots equipped with sensors can detect falls and immediately notify caregivers or emergency services. This can be crucial in preventing serious injuries from falls, which are common among older adults.
- Emergency Assistance: Some robots can respond to emergency situations by alerting family members, caregivers, or emergency responders, ensuring prompt help when needed.
6. Rehabilitation and Therapy
- Physical Therapy Robots: Robots designed for rehabilitation can assist with exercises and movements, helping elderly individuals recover strength and mobility after surgery or illness. They can also guide patients through physical therapy routines tailored to their needs.
- Cognitive Therapy: Some robots use artificial intelligence (AI) to offer cognitive exercises that stimulate the brain, improving memory, focus, and problem-solving skills.
7. Integration with Smart Homes
- Smart Home Systems: Many robots are integrated with smart home devices, allowing them to control lighting, heating, or even assist with shopping and meal preparation. This integration enhances the elderly person’s ability to live independently and safely at home.
- Personalized Alerts: AI-powered robots can learn the routines and preferences of the elderly person, sending reminders for tasks such as taking medications, attending appointments, or completing physical exercises.
Benefits of Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care:
- Increased Independence: Robots can help seniors carry out daily activities and stay independent longer, reducing the need for constant human supervision.
- Improved Quality of Life: By offering companionship, health monitoring, and assistance with tasks, robotics can greatly enhance the mental, emotional, and physical well-being of elderly individuals.
- Caregiver Support: Robotics can ease the workload of family caregivers or healthcare professionals, allowing them to focus on more complex care needs while robots handle routine tasks.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike human caregivers, robots can provide assistance at any time of day or night, ensuring continuous care without breaks.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Cost: High-end robotic systems are often expensive, which may limit their availability to all elderly individuals, especially those on fixed incomes.
- User Acceptance: Some elderly people may be reluctant or uncomfortable with the idea of robots assisting them, especially due to unfamiliarity with technology.
- Ethical Concerns: The introduction of robots in caregiving roles raises ethical questions about privacy, emotional dependency, and the potential for replacing human interaction with machines.
Conclusion:
Advanced robotics for elderly care is transforming the way seniors receive assistance and support, providing a variety of solutions that improve their quality of life, health, and independence. As technology advances, the role of robots in elderly care is likely to expand, offering even more personalized, efficient, and accessible solutions. However, it is important to address the challenges and ethical concerns surrounding the integration of robots into daily life for elderly individuals.
Who is required Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is primarily required by several groups of individuals and organizations who are involved in the care of the elderly. The need for advanced robotics arises from the growing demand to improve the quality of life, safety, and independence of older adults while supporting caregivers. The following groups benefit most from this technology:
1. Elderly Individuals (Seniors)
- People with Chronic Health Conditions: Seniors with conditions like arthritis, diabetes, heart disease, or mobility impairments can benefit from robotic technologies that assist with daily tasks, mobility, and health monitoring.
- Individuals with Cognitive Decline: Those suffering from Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, or other cognitive impairments can benefit from robots that provide social interaction, reminders for medication, and cognitive therapy exercises.
- People with Limited Mobility: Seniors who have difficulty moving or are bedridden due to age-related issues or injuries may rely on robots for assistance with physical activities, like walking, lifting, or transferring.
- Those Living Alone: Older adults living independently may require robotic companions for emotional support, monitoring health, and providing reminders for tasks to ensure safety and well-being.
2. Caregivers
- Family Caregivers: Family members who provide care for elderly loved ones at home may find it difficult to manage the physical, emotional, and logistical demands of caregiving. Advanced robotics can alleviate some of the burdens by assisting with daily tasks like medication management, meal preparation, and mobility assistance.
- Professional Caregivers: Healthcare professionals, including nurses, aides, and geriatric specialists, can benefit from robotic technologies that help manage patient care. Robots can assist in lifting patients, monitoring health metrics, and providing companionship, allowing human caregivers to focus on more complex medical tasks.
3. Healthcare Providers and Facilities
- Hospitals and Clinics: Healthcare facilities that care for elderly patients can use robotics for remote monitoring, telemedicine consultations, and patient mobility. Robots can also assist in performing certain medical tasks like rehabilitation therapy.
- Nursing Homes and Assisted Living Facilities: These institutions care for elderly individuals who require constant supervision and assistance. Robots can help with basic tasks (feeding, medication reminders, mobility assistance) and provide a safer environment by preventing falls and monitoring health.
- Home Healthcare Agencies: Agencies that provide in-home care to elderly patients can incorporate robots into their services to offer support for daily living activities, allowing caregivers to attend to other needs.
4. Research and Development Organizations
- Robotics and AI Researchers: Universities, research institutes, and technology companies are continuously working to develop more effective and efficient robots for elderly care. Researchers focus on improving robot design, AI capabilities, and safety features to meet the evolving needs of the elderly.
- Health and Elder Care Innovators: Companies developing healthcare technologies and elder care solutions are exploring how robotics can be integrated into new products and services. This includes improving rehabilitation devices, creating robotic companions, and designing assistive tools for daily tasks.
5. Government and Policy Makers
- Public Health Organizations: Government bodies and organizations concerned with aging populations, healthcare, and social services are increasingly turning to robotics to meet the needs of seniors. Robots can help reduce the strain on public healthcare systems by providing affordable alternatives to human care for routine tasks.
- Insurance Companies: Insurance providers may be involved in integrating robotic technologies into senior care, as it may reduce the costs associated with long-term care, hospital admissions, or rehabilitation services.
- Aging Population Advocates: Organizations that advocate for the rights and well-being of older adults may support and promote the use of advanced robotics to enhance aging in place and reduce institutionalization.
6. Technology Developers and Manufacturers
- Robotics Engineers and Companies: Companies developing robotics solutions specifically for elderly care (e.g., robotic exoskeletons, health monitoring robots, robotic companions) are focused on meeting the growing demand for advanced, reliable, and affordable care solutions.
- AI and Machine Learning Developers: Companies specializing in AI are integrating machine learning, natural language processing, and advanced algorithms into robots to enhance their ability to assist with cognitive tasks, understand the needs of elderly individuals, and provide more personalized care.
7. Insurance Providers and Long-Term Care Insurance
- Insurance Providers: Insurance companies might support the integration of robotics in elder care as a way to reduce the cost of long-term care and prevent expensive hospitalizations, falls, or accidents.
8. Technology Enthusiasts and Early Adopters
- Tech-Savvy Seniors: Some elderly individuals who are familiar with or open to new technologies may be interested in using advanced robotics to improve their quality of life, manage health conditions, and maintain independence.
- Tech Enthusiasts: This group is interested in the intersection of robotics, AI, and healthcare, particularly for innovative solutions that can help solve social challenges like elder care.
Conclusion:
Advanced robotics for elderly care is needed by elderly individuals themselves, caregivers, healthcare professionals, institutions, researchers, and technology developers. With an aging global population and the increasing challenges faced by elderly individuals in terms of health and mobility, robots offer a practical solution to enhance independence, safety, and quality of life while easing the burden on caregivers and healthcare systems.
When is required Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is required in several situations, especially as the population of older adults continues to grow. The need for advanced robotic solutions is not just limited to certain stages of aging but spans across various life circumstances and health conditions. Here are the key moments or conditions when advanced robotics becomes especially necessary for elderly care:
1. When Seniors Experience Reduced Mobility
- Post-Surgery or Injury Recovery: After surgery or an injury, elderly individuals often struggle with mobility. Advanced robotics can assist in rehabilitation, providing support for movement and exercises.
- Chronic Conditions (e.g., Arthritis, Parkinson’s Disease): Seniors with chronic conditions that affect their ability to move (like arthritis, Parkinson’s disease, or stroke) often require robotic aids like exoskeletons or robotic walkers to maintain mobility and prevent falls.
- Limited Physical Strength: As seniors age, they may lose muscle strength, making it difficult to perform routine tasks. Mobility assistance robots, like powered wheelchairs or robotic walkers, can help them move around more independently.
2. When There Is a Need for Increased Independence
- Living Alone or Aging in Place: Many elderly individuals wish to live independently at home as they age. Advanced robotics can be essential for assisting with activities like cooking, cleaning, taking medications, or reminding the elderly about important tasks.
- Dementia or Alzheimer’s: For individuals experiencing cognitive decline due to dementia or Alzheimer’s disease, robots can offer reminders for medication, appointments, and even assist with cognitive exercises. Robots can also provide companionship, which can help reduce feelings of isolation.
- Loss of Ability to Perform Daily Activities: When elderly individuals begin to struggle with daily activities such as bathing, dressing, eating, or using the bathroom, robots can assist with these tasks, enabling greater independence.
3. During Health Crises or Emergencies
- Health Monitoring and Emergency Response: In cases where seniors suffer from chronic health conditions or are at risk of sudden health events (e.g., heart attacks, strokes), robots equipped with sensors can monitor vital signs and detect any abnormalities. These robots can then alert caregivers or medical professionals in case of an emergency, potentially saving lives.
- Fall Detection: Falls are a significant risk for elderly individuals, leading to severe injuries. Robots equipped with sensors and AI can detect falls, ensuring that help is called immediately, even if the individual cannot reach a phone.
4. When Caregiver Support Is Needed
- When Caregivers Are Overburdened: Family members and professional caregivers often face physical, emotional, and mental exhaustion from caregiving responsibilities. Advanced robotics can alleviate some of the burdens by assisting with basic caregiving tasks like lifting, moving, and providing reminders for medication or personal care.
- Long-Term Care Needs: For seniors who require long-term care due to chronic illness or disability, robotics can help by providing consistent care without the need for a human caregiver to be constantly present. This is especially useful for seniors who live in remote areas or have limited access to medical professionals.
5. When Cognitive and Emotional Support Is Needed
- Social Isolation: Many elderly individuals experience loneliness, which can lead to depression and anxiety. Robots designed for companionship, such as humanoid robots or robotic pets, can offer social interaction, emotional support, and even stimulate mental activity through conversation, games, or memory exercises.
- Mental Health Monitoring: Robots that monitor behavior and emotional well-being can help detect signs of depression, anxiety, or other mental health conditions. By offering companionship and tracking mood patterns, robots can ensure that seniors’ emotional needs are met.
6. When Rehabilitative Care Is Needed
- Physical Therapy: After an injury, surgery, or in cases of muscle weakness due to aging, robots designed for physical rehabilitation can guide seniors through recovery exercises, ensuring that they perform movements correctly and without risk of injury.
- Cognitive Therapy: Robots equipped with AI and specialized programs can provide cognitive exercises that help maintain mental acuity, which is essential for those experiencing early signs of cognitive decline.
7. When There Is a Need for Monitoring and Tracking
- Monitoring Health Metrics: Advanced robots can continuously monitor an elderly person’s health, including vital signs, activity levels, and sleep patterns. This data can be shared with caregivers or medical professionals to provide early warnings about potential health issues.
- Medication Management: Robots can remind elderly individuals to take their medications on time and even dispense the correct dosages. This is crucial for seniors who have difficulty remembering to take their medications, leading to better adherence to treatment plans.
8. When There Is a Desire for Enhanced Safety
- Preventing Falls: Seniors are at high risk of falls, which can lead to severe injuries. Robots can assist in fall prevention by guiding them safely through the home, alerting caregivers when falls occur, and helping them back to a standing position if a fall happens.
- Safety in Smart Homes: In smart home environments, robots can integrate with home automation systems to monitor the safety of seniors by controlling lights, doors, or alarms. For example, a robot could lock doors at night or alert a caregiver if an elderly person wanders from their usual area.
9. When There Are Economic or Systemic Constraints
- Reducing Healthcare Costs: In regions with strained healthcare systems, robots can reduce the need for human caregivers, offering a cost-effective alternative to continuous personal care. This helps alleviate the pressure on public health systems and private long-term care providers.
- Shortage of Caregivers: There is a growing global shortage of professional caregivers. Robotics offers a viable solution to bridge the gap in caregiving availability, especially in remote areas or communities with fewer healthcare resources.
Conclusion:
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is required whenever there is a need for assistance in mobility, health management, daily living activities, social engagement, or caregiver support. As the elderly population grows and faces increased healthcare challenges, robots offer crucial assistance in maintaining independence, enhancing quality of life, and addressing caregiver shortages. The need for these technologies is particularly urgent in cases of health crises, rehabilitation, or when seniors live alone, and it will continue to increase in the future as the demand for elderly care rises globally.
Where is required Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is required in various settings where elderly individuals live, work, or receive care. These locations include homes, healthcare facilities, and community spaces, each benefiting from the use of robotic technology to improve the quality of life, safety, and independence of older adults. Here are the primary places where advanced robotics is required:
1. In Homes (Aging in Place)
- Private Residences: Many seniors prefer to age in place, meaning they want to continue living in their own homes as they grow older. Advanced robotics is required to help them with daily living activities, such as cleaning, cooking, mobility assistance, medication reminders, and emergency response (e.g., fall detection). Robotic solutions like home care assistants, robotic vacuums, and exoskeletons can significantly enhance seniors’ ability to live independently at home.
- Smart Homes for Seniors: In smart homes, robotic systems can integrate with other smart technologies (e.g., automated lighting, alarms, and voice-controlled devices) to provide a safer and more convenient living environment for elderly individuals. These robots can monitor health, prevent falls, and even assist with daily tasks like opening doors or controlling appliances.
2. In Hospitals and Clinics
- Patient Care: Hospitals caring for elderly patients can benefit from robots in a variety of ways. Robots can assist in lifting patients, monitoring health vitals, and supporting rehabilitation. Robotic systems that can track the elderly’s mobility, help with physical therapy, or assist with rehabilitation exercises are increasingly being deployed in medical settings.
- Surgical Assistance: In hospitals, advanced robots are also used for minimally invasive surgeries, helping elderly patients recover more quickly and safely. These robots are highly precise and can reduce the risk of complications during surgeries.
- Telemedicine: Robotic systems in hospitals may also assist in remote healthcare consultations, enabling elderly patients to receive healthcare services without the need to travel, which is particularly useful for individuals with mobility issues.
3. In Nursing Homes and Assisted Living Facilities
- Long-Term Care Homes: Nursing homes and assisted living facilities are environments where elderly individuals who need continuous care live. Robots are used here to assist in providing daily care, help with mobility, and monitor health. Robots can also help manage the administration of medications, track vital signs, or prevent falls.
- Companion Robots: Social robots that provide companionship can be especially valuable in nursing homes, where elderly residents may experience isolation and loneliness. These robots help stimulate conversation, provide reminders, or engage residents in interactive activities, improving their emotional and mental well-being.
- Robotic Caregivers: Robots designed to assist with lifting and transferring patients can reduce the physical strain on human caregivers in nursing homes, allowing staff to focus on more complex care tasks.
4. In Rehabilitation Centers
- Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation: Robotic systems play a critical role in rehabilitation centers, where seniors recover from surgeries, injuries, or illnesses. Robotic exoskeletons and robotic therapy devices can help elderly individuals regain mobility, strength, and function. These systems can assist in physical therapy exercises and track progress over time, offering personalized rehabilitation.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: For elderly patients suffering from cognitive decline (such as Alzheimer’s or dementia), robots are used to provide mental stimulation, track memory, and offer cognitive exercises, supporting rehabilitation efforts for brain health.
5. In Hospitals’ Home Care Services
- Remote Care for Homebound Elderly: In regions where elderly individuals cannot easily access hospitals or clinics, robots can provide remote care services. Robots equipped with telehealth capabilities can allow healthcare professionals to remotely monitor elderly patients’ health and guide them through exercises or medication routines.
- Home Health Monitoring: Robotic technologies are required in home health monitoring systems, where they assist healthcare providers in managing elderly patients’ chronic conditions. These systems can monitor vitals, report changes in health status, and alert healthcare professionals to take action when necessary.
6. In Community and Senior Centers
- Senior Socialization Spaces: Robotics can be used in senior community centers to offer social engagement, health monitoring, and wellness activities. Robots may provide entertainment, help with interactive games, or assist in exercise classes.
- Assistance in Public Spaces: In places where elderly people gather, like community centers or libraries, robots can help by guiding them to different areas, offering informational assistance, or ensuring their safety in large or complex environments.
7. In Public Spaces and Transport Systems
- Transport Assistance: Public transport systems can also be equipped with robots to assist elderly passengers with boarding, navigation, and carrying bags. Robotic systems could also be deployed in taxis or ride-sharing services, helping elderly individuals get in and out of vehicles more easily.
- Public Assistance Robots: In public spaces like shopping malls, airports, or train stations, robots can be used to help elderly people with navigation, carrying heavy loads, or locating specific areas, ensuring they can move around comfortably.
8. In Research and Development Facilities
- Universities and Robotics Labs: Research institutions, universities, and robotics companies are key locations where robotics technologies for elderly care are developed and tested. Advanced robotics for elder care is continuously evolving, and these centers are essential for creating and improving robots that can be used in homes, hospitals, and care facilities.
- Testing New Robotic Solutions: As part of the innovation process, robots for elderly care are trialed and tested in controlled environments, ensuring that they meet the necessary safety, reliability, and user experience standards before being deployed in real-world settings.
9. In Emergency Services and Disaster Relief
- Emergency Robotics: During disasters or emergencies, robots can assist elderly individuals who are unable to evacuate or require urgent medical care. Robots with mobility, communication, and medical support capabilities can provide vital help to elderly people in emergency situations.
10. In Technology-Powered Elder Care Ecosystems
- Health Monitoring Systems: Advanced robotic systems integrated into larger health monitoring ecosystems, including smart home devices, wearable health monitors, and remote monitoring stations, are critical in ensuring the elderly are consistently supported across various care settings.
- AI-Integrated Robotics for Caregiving: Robotics that integrate artificial intelligence can be placed in any of these environments to continuously learn and adapt to the needs of elderly individuals, improving their daily lives and safety.
Conclusion:
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is required in homes, hospitals, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, public spaces, research facilities, and emergency services, among others. Wherever elderly individuals reside, receive care, or require assistance, robots can play a critical role in ensuring their safety, independence, and well-being. With the increasing aging population and the growing demand for care services, these advanced robotic systems are becoming an essential part of elderly care across a wide range of environments.

How is required Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is required in several ways to improve the quality of life, independence, and overall well-being of older adults. As the elderly population grows worldwide, there is an increasing demand for innovative solutions that can assist with the physical, emotional, and medical needs of seniors. Robotics plays a vital role in filling gaps in caregiving, addressing issues like mobility, safety, social isolation, and chronic illness management.
Here’s how advanced robotics is required for elderly care:
1. Physical Assistance
- Mobility Support: Many elderly individuals experience decreased mobility due to conditions like arthritis, stroke, or general aging. Robots, such as exoskeletons or mobility assistive robots, help seniors maintain or regain their ability to walk and move independently. These devices can assist with standing, walking, and sitting, thereby reducing the need for human caregivers.
- Lifting and Transfer: Robots designed for lifting and transferring elderly people can assist in moving them from beds to chairs, wheelchairs, or cars without causing physical strain on caregivers. These robots ensure the safety and comfort of both the elderly and their caregivers by preventing injuries from improper lifting techniques.
- Personal Care Robots: Robots that help with personal hygiene tasks such as bathing, dressing, and grooming are essential for elderly individuals who have limited mobility or physical limitations. This reduces the need for full-time human assistance, ensuring greater privacy and dignity for the elderly.
2. Safety and Monitoring
- Fall Detection and Prevention: Falls are one of the leading causes of injury and death in older adults. Advanced robotics integrated with sensors and AI can detect falls in real-time and alert caregivers or emergency services. Some robots are also designed to help prevent falls by monitoring an elderly person’s movements and offering stability support when needed.
- 24/7 Monitoring: Robots can be equipped with sensors to monitor an elderly individual’s health, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. This constant monitoring provides caregivers and healthcare providers with critical information, enabling early intervention if necessary. Robots can also track patterns of behavior, alerting caregivers to signs of distress, changes in routine, or other concerns.
- Emergency Assistance: In emergencies, robots can provide assistance by offering communication tools, navigating the home to locate the elderly person, or even providing basic first aid. They can also guide elderly individuals to exits during evacuations or natural disasters.
3. Medication Management
- Medication Reminders: Robots can be programmed to remind elderly individuals to take their medications at specific times. Some robots even have the capability to dispense medications, ensuring proper dosages are taken. This reduces the risk of medication errors and improves adherence to prescribed health regimens.
- Monitoring Health Indicators: Many robotic systems are designed to track health metrics such as glucose levels (for diabetes management), heart rate, or respiratory function. This constant monitoring ensures that caregivers or medical professionals can respond promptly to health changes.
4. Emotional and Social Support
- Companion Robots: Loneliness is a major issue for many elderly individuals, especially those living alone or in long-term care facilities. Robots can provide companionship by engaging in conversations, playing games, or even offering reminders for daily routines. Some robots are designed with AI that allows them to recognize and respond to emotional cues, providing tailored interactions to improve mental well-being.
- Cognitive Engagement: Robots can help engage elderly individuals in cognitive exercises that help prevent cognitive decline or dementia. For example, robots can lead memory games, puzzles, or interactive activities designed to stimulate the mind and promote mental health.
5. Assistive Communication
- Telepresence and Communication Robots: For elderly individuals with limited mobility or hearing/speech impairments, communication robots allow them to engage with loved ones and caregivers remotely. These robots can act as a virtual presence, helping seniors connect with family, friends, or doctors even if they cannot leave their homes or rooms.
- Speech and Language Assistance: Robots with speech recognition and synthesis capabilities can assist seniors who have difficulty speaking or understanding others. These robots can communicate with elderly individuals, allowing them to give commands or express needs without relying on human assistance.
6. Healthcare and Rehabilitation
- Robotic Rehabilitation: For elderly individuals recovering from surgery, strokes, or other physical impairments, robots can assist in rehabilitation. Robotic exoskeletons and therapy robots can help guide patients through physical therapy exercises, ensuring proper form and offering real-time feedback. These robots can adapt to each individual’s progress, providing personalized rehabilitation programs.
- Remote Health Monitoring: With advancements in telemedicine, robots can play a role in remote consultations, helping elderly patients connect with doctors or health professionals without needing to travel. Robots equipped with sensors can track and share vital health data, allowing healthcare providers to monitor patients from afar.
7. Enhancing Caregiver Support
- Reducing Caregiver Burnout: Robots are a valuable tool in alleviating the workload of human caregivers by assisting with repetitive or physically demanding tasks, such as lifting, moving, or monitoring patients. By reducing the burden on human caregivers, robots allow them to focus on providing more personalized care, and this helps reduce burnout and fatigue.
- Robotic Assistance for Home Caregivers: Family members who provide care for elderly relatives can also benefit from robotic assistance. Robots can help family caregivers by taking over certain tasks, offering companionship to seniors, and allowing caregivers to focus on other responsibilities or self-care.
8. Personalized and Adaptive Care
- Artificial Intelligence Integration: Robots designed for elderly care can utilize AI to learn the needs and preferences of the individual they are assisting. This adaptability allows robots to provide more personalized care over time, such as recognizing patterns in behavior or health conditions, and adjusting their actions accordingly.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: With AI and machine learning, robots can analyze data gathered over time to optimize care plans, offer insights into an elderly person’s condition, and suggest improvements to caregiving strategies.
9. Independence and Quality of Life
- Encouraging Autonomy: Robots that help with daily activities like cooking, cleaning, and even grocery shopping enable elderly individuals to remain independent for longer. By assisting with these tasks, robots promote autonomy and ensure that seniors can continue living in their homes with dignity and freedom.
- Recreational Robots: Robots can also assist in recreational activities such as interactive games, arts and crafts, or light exercise routines, encouraging seniors to stay active and engaged.
Conclusion:
Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care is required to assist elderly individuals in living safer, healthier, and more independent lives. These technologies can address a wide range of challenges faced by the elderly, from physical limitations and health monitoring to emotional support and social isolation. Robotics in elderly care provides both the elderly and their caregivers with more options, allowing for improved quality of life, reduced caregiver burden, and enhanced care capabilities.
Case study is Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Case Study: Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care
Background
The elderly population is rapidly increasing worldwide, leading to higher demand for long-term care, home assistance, and medical services. Traditional caregiving, although essential, is often limited by human resource constraints, caregiver burnout, and the physical limitations of elderly individuals. This scenario has made advanced robotics a viable solution for assisting the elderly with daily activities, ensuring safety, providing companionship, and improving their quality of life.
This case study explores the use of advanced robotics in elderly care, focusing on a real-life implementation of robotics at a retirement home in Japan, a country known for its rapidly aging population.
Project Overview: “ElderCare Robotics Initiative”
Location: Tokyo, Japan
Facility: Sakura Senior Living, a private retirement home
Objective: To enhance elderly care through advanced robotics, focusing on improving mobility, independence, safety, and social engagement.
Technologies Used
- Robotic Assistants for Mobility and Lifting
- Robotic Exoskeletons: Devices worn by elderly residents to assist with walking, standing, and sitting, particularly for those suffering from mobility impairments.
- Lifting Robots: Robots designed to help caregivers safely lift and transfer residents from beds to chairs or other surfaces, reducing the risk of injury for both seniors and caregivers.
- Companion Robots for Emotional Support
- PARO Robot: A therapeutic robot designed to mimic the appearance and behavior of a baby seal. It is used for emotional support and companionship, reducing loneliness and promoting mental well-being.
- Softbank Robotics’ Pepper: A humanoid robot designed to interact with elderly residents. Pepper communicates, performs simple tasks, and provides reminders about medication and activities.
- Health Monitoring and Emergency Response Robots
- Sensor-Based Robots: Robots equipped with motion and health sensors to track the vital signs of residents (e.g., heart rate, temperature) and detect emergencies, such as falls.
- Emergency Assistance Robots: Robots that can alert healthcare professionals in case of an emergency, providing a timely response.
Implementation Process
- Phase 1: Initial Assessment and Integration
- Assessment: The management of Sakura Senior Living conducted a thorough assessment of the facility’s needs, identifying areas where robotics could improve care. This included mobility challenges, fall prevention, medication management, and emotional support.
- Robot Selection: Based on the needs assessment, the facility decided to integrate a combination of robotic exoskeletons, companion robots, and health monitoring systems. The robots were selected for their ease of use, compatibility with the residents’ physical needs, and ability to integrate into existing caregiving workflows.
- Phase 2: Training and Deployment
- Staff Training: Caregivers and healthcare staff underwent comprehensive training on how to use and maintain the robots. This included operational training, troubleshooting, and understanding the data generated by robots (e.g., health metrics, activity logs).
- Pilot Program: The robots were introduced to a small group of residents for a period of 3 months. The feedback from both residents and caregivers was gathered to assess the effectiveness of the robots.
- Phase 3: Evaluation and Optimization
- Resident Feedback: Residents expressed satisfaction with the companionship robots, such as PARO and Pepper, which helped alleviate feelings of isolation. The robots’ ability to interact, play games, and engage in conversations helped boost morale and emotional well-being.
- Caregiver Feedback: Caregivers found the mobility and lifting robots significantly reduced physical strain and minimized the risk of injury during transfers. The robots also allowed them to focus more on providing personalized care.
- Health Monitoring and Safety: The sensor-based robots played a crucial role in monitoring residents’ health and ensuring their safety. Fall detection sensors and emergency alerts were critical in identifying health crises early, leading to timely interventions.
- Phase 4: Full Integration
- After the pilot program’s success, the facility decided to fully integrate the robots into daily operations. The robots became part of the routine care for residents, with regular maintenance and software updates ensuring optimal performance.
Results and Impact
- Improved Mobility and Independence
- Residents using robotic exoskeletons reported increased mobility and a sense of independence. Those with limited walking ability were able to stand, walk, and move more freely, improving their overall quality of life.
- Some elderly residents who were previously confined to wheelchairs regained their ability to walk with the help of exoskeletons.
- Reduced Caregiver Burden
- Caregivers experienced a significant reduction in physical strain and risk of injury due to the use of lifting robots. These robots allowed for smoother, safer transfers, reducing caregiver fatigue and improving job satisfaction.
- Enhanced Emotional Well-being
- The PARO robot was a huge success, with many residents reporting a sense of companionship and emotional comfort. The robot’s interactions provided emotional support, reducing anxiety and depression among residents, particularly those with dementia.
- Pepper the robot contributed to daily routines by providing reminders and offering simple interactions, helping residents feel more engaged and connected.
- Improved Health Monitoring and Emergency Response
- The health monitoring robots allowed the facility to track real-time health data for residents, including monitoring vital signs and detecting abnormalities. This proactive approach resulted in fewer medical emergencies and allowed staff to provide prompt interventions when needed.
- Fall detection and emergency response capabilities reduced the number of serious injuries resulting from falls. In cases of emergencies, the robots immediately alerted healthcare providers, enabling faster response times.
- Cost Savings and Long-term Viability
- The initial investment in robotics technology was offset by long-term savings in healthcare costs and labor. The facility saw reduced hospitalization costs due to early detection of health issues and fewer injuries to both residents and caregivers.
- Robots also helped manage staff shortages, allowing caregivers to spend more time providing personal care rather than performing physically demanding tasks.
Challenges and Limitations
- High Initial Costs: The upfront cost of advanced robotic systems, including exoskeletons, companion robots, and health monitoring systems, was significant. However, the long-term savings and positive outcomes justified the investment.
- Technology Acceptance: Some elderly residents were initially hesitant to interact with robots, especially those with cognitive impairments. Over time, caregivers played a crucial role in helping residents become more comfortable with robotic assistance.
- Maintenance and Upkeep: Regular maintenance, software updates, and troubleshooting were essential for the robots to function effectively. The facility needed to ensure technical support was readily available.
Conclusion
The ElderCare Robotics Initiative at Sakura Senior Living demonstrated the potential of advanced robotics to significantly enhance elderly care. By integrating robotic mobility aids, companion robots, and health monitoring systems, the facility was able to improve both the physical and emotional well-being of its residents while reducing the burden on caregivers. As the global elderly population continues to grow, the success of this initiative provides a compelling case for the widespread adoption of robotics in elderly care settings.
White paper on Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
White Paper: Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care
Executive Summary
The global population is aging at an unprecedented rate, leading to increasing demands for elderly care services. Robotics technology has emerged as a transformative solution, providing innovative tools to enhance the quality of life for older adults. This white paper explores the role of advanced robotics in elderly care, discussing its applications, benefits, challenges, and future potential. By examining current technologies and case studies, we aim to demonstrate how robotics can address the challenges of elderly care and contribute to more efficient, safe, and compassionate environments for aging populations.
Introduction
The elderly population worldwide is growing rapidly due to increasing life expectancy, advancements in healthcare, and improved living standards. According to the United Nations, by 2050, one in six people in the world will be over the age of 65, and the number of people aged 80 or older is expected to triple. This demographic shift presents significant challenges for elderly care systems, including caregiving shortages, rising healthcare costs, and the increasing need for specialized care.
Robotic technologies offer solutions to these challenges by enhancing physical mobility, providing emotional support, and ensuring safety for elderly individuals. These systems can reduce the burden on human caregivers, improve independence for the elderly, and address the rising demand for long-term care.
Applications of Advanced Robotics in Elderly Care
1. Robotic Mobility Assistants
- Exoskeletons: Wearable robotic exoskeletons assist elderly individuals with limited mobility. These devices provide support to help them stand, walk, and perform daily tasks with greater independence. By augmenting the wearer’s strength, exoskeletons can assist individuals with conditions like arthritis, stroke, or muscular dystrophy.
- Wheelchairs and Walking Robots: Autonomous and semi-autonomous robotic wheelchairs are designed to move freely within a home or healthcare facility, allowing elderly users to navigate spaces without assistance. These robots can be programmed to follow specific routes, avoid obstacles, and respond to voice commands.
2. Companion Robots
- Social Interaction: Robots such as PARO, a therapeutic robot designed to look like a baby seal, provide companionship to elderly individuals, especially those with dementia or Alzheimer’s disease. These robots engage in simple interactions like responding to touch and sound, offering emotional support, reducing anxiety, and alleviating loneliness.
- Humanoid Robots: Robots like Pepper, designed by SoftBank Robotics, engage elderly residents in conversations, play games, provide reminders for medication, and perform basic tasks. These robots are increasingly integrated into elder care facilities to offer companionship, mental stimulation, and task management.
3. Health Monitoring and Safety Robots
- Health Sensors: Robots equipped with biosensors monitor vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature. These devices alert caregivers and medical professionals in case of any abnormal readings, enabling timely intervention and reducing the risk of medical emergencies.
- Fall Detection Systems: Robots are equipped with sensors to detect falls or other emergency situations. When a fall is detected, the robot immediately alerts caregivers or healthcare providers, reducing response times and improving outcomes for elderly individuals.
- Medication Reminders: Robotic assistants can remind elderly individuals to take their medication at the correct times, ensuring adherence to prescribed regimens and reducing the likelihood of missed doses.
4. Robotic Caregivers and Assistance
- Lifting and Transfer Robots: Lifting robots assist caregivers in transferring elderly patients from one place to another (e.g., from bed to chair), reducing the physical strain on caregivers and minimizing the risk of injury to both parties. This helps facilitate more dignified care for elderly individuals with limited mobility.
- Robotic Assistants for Daily Tasks: Robots can help with daily tasks such as cleaning, cooking, and personal care activities, providing additional support for elderly individuals who prefer to live independently but need assistance with certain activities.
Benefits of Advanced Robotics in Elderly Care
1. Improved Quality of Life
Robots can enable elderly individuals to maintain their independence and continue to engage in activities they enjoy. By assisting with physical tasks, providing emotional companionship, and offering social interaction, robots enhance the overall well-being of elderly people.
2. Increased Safety and Security
The use of robotics in elderly care improves safety by monitoring vital signs, detecting falls, and ensuring that help is always available in case of emergencies. The integration of robots equipped with fall detection and health-monitoring sensors can significantly reduce the risk of injuries and medical complications.
3. Reduction in Caregiver Burden
Robotic systems reduce the physical and emotional strain on caregivers, allowing them to focus on more complex aspects of care. By automating repetitive or physically demanding tasks such as lifting and transporting patients, robots help mitigate caregiver burnout and address workforce shortages in elder care.
4. Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in robotic technology can be high, robots can offer long-term cost savings by reducing hospital admissions, preventing falls, and decreasing the need for human intervention in routine tasks. Robotics can also contribute to optimizing resource allocation, allowing human caregivers to spend more time on personal care.
5. Personalized and Adaptive Care
Advanced robotics can be tailored to meet the specific needs of individual elderly patients. Adaptive robots can adjust their behavior based on user preferences, making them ideal for personalized care. They can monitor health metrics over time and suggest interventions when necessary, providing a more responsive care model.
Challenges and Limitations
1. High Initial Cost
The upfront cost of robotic systems, including development, purchase, and installation, can be prohibitively expensive for many elderly care facilities or individual homes. However, the long-term benefits may outweigh the costs, particularly when factoring in the reduction of labor and healthcare-related expenses.
2. Acceptance and Comfort
The integration of robots into elderly care environments may face resistance from both the elderly individuals and their families. Many elderly people may feel uncomfortable with technology or hesitant to trust robots for personal care. Overcoming such reluctance requires proper training, education, and gradual integration into daily routines.
3. Technical Limitations
Robotics technologies are not yet perfect. Issues such as hardware malfunctions, software bugs, or difficulties in adapting to complex, unstructured environments can hinder the smooth functioning of robots. Regular maintenance and updates are essential for the reliable operation of robotic systems.
4. Privacy Concerns
The use of sensors and data collection in elderly care robots raises concerns about privacy and data security. It is essential to ensure that sensitive health information is protected and that appropriate safeguards are in place to prevent unauthorized access to personal data.
Future Outlook
The future of robotics in elderly care is promising, with continuous advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and sensor technologies. Future robots will become more autonomous, intuitive, and capable of performing a wider range of tasks, including complex healthcare procedures.
As the aging population continues to grow, it is likely that the demand for robotic assistance in elderly care will increase. Governments, healthcare providers, and technology companies will need to collaborate to drive innovation, reduce costs, and make robotic care more accessible to elderly individuals worldwide.
Conclusion
Advanced robotics has the potential to revolutionize elderly care by improving safety, enhancing quality of life, and reducing the burden on caregivers. Through the application of mobility assistants, companion robots, health monitoring systems, and caregiving robots, these technologies can address the challenges posed by an aging global population. Despite some challenges, the long-term benefits of robotics in elderly care make it a promising and necessary solution for the future of healthcare.
As the field continues to evolve, it is critical to address issues of cost, acceptance, and privacy to ensure that robotics can be fully integrated into elderly care environments. The ongoing development and adoption of robotics technologies will play a crucial role in meeting the needs of the elderly and ensuring that they receive the care and support they deserve.
Industrial application of Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Industrial Applications of Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care
Advanced robotics for elderly care is not only a promising solution for healthcare systems but also has significant industrial applications that can transform how society addresses the aging population’s needs. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and technology are actively developing robotic systems designed to improve elderly care. Below are several key industrial applications of advanced robotics in elderly care.
1. Healthcare and Medical Robotics
a. Surgical Robotics
- Robotic Surgery Assistants: Robotic surgery systems like da Vinci Surgical System are already being used for minimally invasive procedures. These robots offer precision and flexibility, allowing surgeons to perform delicate operations with higher accuracy. In elderly care, they can be used for procedures such as joint replacements, heart surgeries, and cancer treatments, reducing recovery time and improving patient outcomes.
b. Rehabilitation Robotics
- Exoskeletons and Assistive Devices: Industrial robots are being developed to aid in rehabilitation for elderly individuals suffering from conditions such as stroke, spinal cord injuries, or neurological diseases. Rehabilitation exoskeletons, like ReWalk, assist users in regaining the ability to walk by providing external support. This helps elderly individuals maintain mobility and prevent the deterioration of muscle mass and bone density.
c. Remote Patient Monitoring
- Telemedicine and Robotics Integration: Robots equipped with health monitoring systems can track vital signs (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure) and provide continuous data to healthcare providers. Telepresence robots (e.g., Double Robotics) allow medical professionals to remotely interact with elderly patients in real-time, enabling regular check-ups without the need for the patient to travel to a clinic or hospital.
2. Assisted Living and Elderly Care Facilities
a. Autonomous Care Robots
- Personal Care Robots: In nursing homes or assisted living facilities, robots such as Robear or Buddy help caregivers with routine tasks, such as lifting patients, assisting with mobility, and providing emotional companionship. These robots enhance the autonomy of elderly individuals, allowing them to carry out daily activities like getting out of bed, dressing, and eating with minimal assistance.
b. Companion Robots for Social Interaction
- Social and Cognitive Engagement: Robots like PARO (a therapeutic robot resembling a baby seal) and Pepper (a humanoid robot) are designed to provide emotional support, stimulate cognitive function, and prevent loneliness in elderly people. They are widely used in long-term care facilities to interact with residents, engage them in activities, and even monitor their emotional and mental health.
c. Monitoring and Security Systems
- Fall Detection and Emergency Response: Robots in elderly care facilities are equipped with fall detection sensors, allowing them to monitor the environment and alert caregivers in case of emergencies. Robotic security systems, including autonomous drones and patrolling robots, provide safety monitoring in residential care environments. These robots can detect potential hazards and prevent accidents by alerting human supervisors immediately.
3. Smart Home Robotics
a. Home Assistants for the Elderly
- Voice-controlled Assistants: Smart home robots, integrated with AI and voice recognition, such as Amazon Alexa or Google Assistant, can help elderly individuals control their home environment. These robots enable the elderly to manage lighting, temperature, and security systems through voice commands, making it easier for them to live independently.
b. Cleaning and Maintenance Robots
- Robotic Vacuum Cleaners and Moppers: In home environments, robots like iRobot Roomba or Ecovacs Deebot are increasingly being used by elderly individuals to maintain cleanliness with minimal effort. These robots autonomously clean floors, carpets, and even mop surfaces, which can be physically taxing for the elderly.
c. Medication Management Robots
- Automated Medication Dispensers: Robots like MedMinder and Pillo help elderly individuals manage their medication schedules. These robots can remind individuals to take their medication, dispense the correct dosage, and even alert caregivers if a dose is missed. This ensures that elderly patients adhere to prescribed treatments, reducing the risk of medical complications.
4. Industrial Automation in Elderly Care Technology
a. Manufacturing of Elderly Care Products
- Robot-Assisted Manufacturing: Robotics are heavily involved in the manufacturing of elderly care products such as assistive devices (e.g., wheelchairs, walkers), medical supplies, and mobility aids. Industrial robots are used to assemble these products with precision and efficiency, ensuring higher product quality and reducing production time.
b. Service Robots in Public Spaces
- Delivery and Assistance Robots: Industrial robots such as serve robots can be deployed in nursing homes, hospitals, and public spaces to deliver meals, medications, or other supplies. For example, Bear Robotics’ Servi robot is used in long-term care facilities to assist staff with meal delivery, allowing elderly residents to receive food promptly without the need for staff to enter their rooms.
c. Maintenance Robotics in Elderly Care Environments
- Robotic Inspection and Maintenance: Robots used for inspection and maintenance, like autonomous cleaning systems or robots that monitor building infrastructure, can ensure that elderly care facilities are safe and well-maintained. These systems help with routine maintenance tasks, reducing the need for human labor and ensuring that facilities meet safety standards.
5. Research and Development for Elderly Care Robotics
a. Development of AI Algorithms for Personalization
- AI-driven Robotics for Elderly Needs: Advanced robotics used in elderly care are increasingly integrated with AI and machine learning algorithms to personalize care. Robots can adapt their behaviors and responses based on the specific needs, preferences, and health conditions of the elderly person they assist. This can include tailored exercise routines, cognitive games, or customized social interaction patterns based on the individual’s cognitive health.
b. Human-Robot Interaction Research
- Ergonomics and Comfort: Ongoing research in human-robot interaction focuses on making robots more intuitive, comfortable, and adaptable to elderly users. Industrial applications involve studying how robots can better communicate with elderly individuals, offer emotional support, and be physically accessible to users with varying degrees of mobility and cognitive function.
Challenges in the Industrial Application of Robotics for Elderly Care
While the industrial applications of robotics in elderly care are vast, several challenges need to be addressed:
- Cost and Affordability: Robotics technology for elderly care is often expensive, making it inaccessible to many elderly individuals or care institutions, especially in developing regions.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of robots in elderly care raises concerns about privacy, autonomy, and the potential for social isolation. Ethical frameworks are needed to guide the responsible integration of robots into care settings.
- Technological Limitations: Many elderly individuals are not comfortable with advanced technology. Ensuring that robots are user-friendly, intuitive, and easy for the elderly to operate is critical for successful adoption.
- Regulatory and Safety Standards: The robotics industry for elderly care needs to meet high safety standards to ensure that robots do not harm the elderly individuals they are intended to assist. This requires stringent regulatory oversight and robust testing protocols.
Conclusion
The industrial application of advanced robotics for elderly care holds immense potential to transform the caregiving landscape by enhancing the quality of life for elderly individuals, improving safety, and easing the burden on human caregivers. From medical robots and rehabilitation devices to home assistants and caregiving robots, the integration of advanced robotics in elderly care settings is rapidly expanding.
However, challenges such as cost, ethical concerns, and technological limitations must be addressed to fully realize the benefits of robotics in elderly care. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that robots will play an even more significant role in the future of elderly care, offering personalized, efficient, and compassionate solutions to the challenges posed by an aging global population.
Research and development of Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care ?
Research and Development of Advanced Robotics for Elderly Care
The research and development (R&D) of advanced robotics for elderly care has grown significantly over the past few years. As the global population ages, there is an increasing demand for innovative technologies that can assist elderly individuals in living healthier, more independent lives while alleviating the strain on healthcare systems and caregivers. Researchers and engineers worldwide are working on developing cutting-edge robotics solutions aimed at improving various aspects of elderly care. Below are the key areas of research and development in this field.
1. Assistive Robotics for Daily Activities
a. Mobility Assistance Robots
- Objective: The development of robots that help elderly individuals with mobility issues is a key area of R&D. These robots can assist with walking, getting out of bed, standing, or sitting, helping elderly people retain their independence while reducing the risk of falls.
- Example: Exoskeletons and robotic walkers (e.g., Honda’s Walking Assist Device, ReWalk) are being developed to enable elderly users to walk or stand, providing support for those with mobility impairments caused by conditions such as arthritis, stroke, or neurological diseases.
b. Robotic Arms and Assistive Devices
- Objective: Robotic arms can help elderly individuals with limited arm strength or mobility perform everyday tasks, such as eating, dressing, or reaching high shelves. R&D is focused on designing lightweight, user-friendly robots that can seamlessly integrate into the daily lives of elderly users.
- Example: Robotic arms (e.g., RoboTable) designed for elderly individuals assist them in feeding themselves, particularly those with tremors or severe motor impairments. The system features sensors to adjust to the user’s movements and provide steady assistance.
2. Social Interaction and Cognitive Assistance
a. Social Companion Robots
- Objective: Social isolation is a significant problem for the elderly, leading to depression and cognitive decline. Robots designed to provide companionship and emotional support are becoming a major area of research.
- Example: PARO (a therapeutic robot resembling a baby seal) is designed to mimic the behavior of a pet and provide emotional comfort to elderly individuals. Research is ongoing to improve the robot’s ability to respond to voice commands and simulate lifelike interactions.
b. Cognitive Engagement and Memory Care
- Objective: Cognitive decline, such as that caused by Alzheimer’s or dementia, is a common challenge among the elderly. Robotic systems are being developed to stimulate the mind and provide mental exercises.
- Example: Pepper, a humanoid robot developed by SoftBank, is designed to interact with elderly individuals through conversation, games, and cognitive exercises. Researchers are enhancing the robot’s ability to engage elderly individuals in conversations and memory games, improving their mental well-being.
3. Healthcare and Medical Robotics
a. Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
- Objective: As healthcare becomes more reliant on digital technologies, robotics plays a crucial role in remote healthcare delivery. Telepresence robots allow healthcare professionals to remotely monitor and interact with elderly patients in real-time.
- Example: Telerobotic systems allow doctors to conduct virtual consultations, while robots like Aethon TUG can transport medications, clean, or deliver supplies within healthcare facilities, thus reducing the workload of caregivers and hospital staff.
b. Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation
- Objective: Robots designed to assist with rehabilitation help elderly patients recover mobility, strength, and cognitive functions following a stroke, surgery, or injury. R&D efforts focus on creating more adaptive and personalized rehabilitation systems.
- Example: Rehabilitation exoskeletons such as EksoGT and Indego help individuals with lower-body paralysis stand, walk, or move with minimal effort, improving physical recovery after neurological impairments.
4. Fall Detection and Safety Systems
a. Autonomous Fall Detection and Response Systems
- Objective: Fall prevention and detection are critical aspects of elderly care. Fall detection systems using sensors and robots are being developed to automatically detect when a person falls and alert caregivers or medical professionals immediately.
- Example: Robotic systems integrated with advanced sensors (e.g., RoboCare, FallBot) can identify a fall or accident and automatically contact emergency services or caregivers. These robots may also be equipped with advanced AI to assess the situation and react appropriately.
b. Hazard Detection and Prevention
- Objective: In addition to detecting falls, research is being conducted to create robots that can identify and prevent hazards such as slippery floors, obstacles, or unclean environments in the homes of elderly individuals.
- Example: Smart home robots like Intuition Robotics use AI and sensors to monitor environments, prevent falls, and ensure elderly people’s living spaces are safe and accessible.
5. Smart Homes and Integrated Robotics Systems
a. Smart Home Integration
- Objective: The integration of robotics with smart home systems aims to improve elderly care by automating home functions like lighting, temperature control, and security. R&D is focused on creating seamless systems that allow elderly individuals to interact with their homes using voice commands, gestures, or mobile apps.
- Example: Robotic home assistants such as Amazon Echo or Google Home integrate with other home devices and robots, enabling elderly individuals to control their environment and access emergency assistance simply by asking.
b. Autonomous Delivery and Household Assistance
- Objective: Research is exploring robots that can autonomously assist with tasks such as delivering meals, medications, or groceries. These robots can also help clean the home, assist with laundry, and perform other tasks to enhance the elderly person’s quality of life.
- Example: Service robots like Bear Robotics’ Servi deliver meals to elderly patients in hospitals or care homes. Similarly, autonomous vacuuming and cleaning robots are becoming increasingly popular for elderly users.
6. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Elderly Care
a. Personalized Care through AI
- Objective: The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in robotics for elderly care focuses on personalization. AI algorithms can learn an elderly individual’s routines, preferences, and health conditions, adjusting robotic behavior to provide customized assistance.
- Example: AI-powered caregiving robots such as ElliQ (developed by Intuition Robotics) are designed to offer personalized interactions, suggesting activities, reminding individuals of tasks, or simply keeping them company. These robots are also capable of learning from interactions to better understand the needs of elderly users.
b. Data-Driven Health Monitoring
- Objective: AI and machine learning models are being integrated into robotic systems to continuously monitor the health status of elderly individuals. These systems can detect early signs of illness, track vital signs, and predict potential health risks, allowing for early intervention.
- Example: Smart wearable robots with AI capabilities are used to monitor an elderly person’s health metrics such as heart rate, blood pressure, and temperature. These robots can trigger alerts if any health anomalies are detected, enabling caregivers to respond quickly.
7. Ethical and Human-Robot Interaction Research
a. Human-Robot Interaction (HRI)
- Objective: One critical aspect of robotic systems for elderly care is ensuring that robots interact effectively and safely with humans. Researchers focus on making robots more intuitive, empathetic, and user-friendly to facilitate smoother communication with elderly users.
- Example: HRI research is exploring ways to make robots respond to emotional cues, adapt to human gestures, and engage in natural conversations. These robots must also address issues of trust, safety, and comfort for elderly individuals who may be wary of new technology.
b. Ethical Issues and Autonomy
- Objective: The ethical implications of using robots for elderly care, including concerns about privacy, autonomy, and the potential for social isolation, are a major research focus. Ensuring that elderly people feel empowered, rather than dependent on robots, is a key challenge.
- Example: Ethical guidelines are being developed to ensure that robots are used in ways that respect the autonomy and dignity of elderly individuals. These guidelines address issues such as data security, informed consent, and human-robot relationships.
Conclusion
Research and development in the field of advanced robotics for elderly care is progressing rapidly, with innovations aimed at addressing the challenges of an aging population. From mobility and rehabilitation to social companionship and healthcare monitoring, robotics is being tailored to meet the diverse needs of elderly individuals.
However, challenges remain in terms of ensuring affordability, accessibility, and ethical considerations. As technology advances and new breakthroughs emerge, the integration of robotics into elderly care will likely become more prevalent, making it a vital component of the future healthcare ecosystem.
Courtesy : Supercar Blondie
References
- ^ “Companion Robots Are Here. Just Don’t Fall in Love With Them”. WIRED. Retrieved 2018-07-05.
- ^ “Robot caregivers are saving the elderly from lives of loneliness”. Engadget. Retrieved 2018-07-05.
- ^ Wang, Kelly. “‘iPal’ robot companion for China’s lonely children”. phys.org. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ Dautenhahn, K.; Woods, S.; Kaouri, C.; Walters, M.L.; Kheng Lee Koay; Werry, I. (2005). “What is a robot companion – friend, assistant or butler?”. IEEE. pp. 1192–1197. doi:10.1109/IROS.2005.1545189. ISBN 0-7803-8912-3. Retrieved 2005-12-05.
- ^ “Towards personal service robots for the elderly”. Workshop on Interactive Robots and Entertainment. 25. 2000.
- ^ halusker (2023-10-25). “The rise of robotic companions to address social isolation”. Center for Healthy Aging. Retrieved 2024-04-22.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Paro”. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Xiong, Caihua; Huang, Yongan; Xiong, Youlun (2008). Intelligent Robotics and Applications: First International Conference, ICIRA 2008 Wuhan, China, October 15-17, 2008 Proceedings. Berlin: Springer. pp. 538–539. ISBN 9783540885122.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Lamers, Maarten H.; Verbeek, Fons J. (2011). Human-Robot Personal Relationships: Third International Conference, HRPR 2010, Leiden, The Netherlands, June 23-24, 2010, Revised Selected Papers. Heidelberg: Springer Science & Business Media. p. 13. ISBN 9783642193842.
- ^ “CompanionAble”. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ Wang, Kelly. “‘iPal’ robot companion for China’s lonely children”. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Saint-Aime, Sebastien; Le-Pevedic, Brigitte; Duhaut, Dominique; Shibata, Takanori (2007). EmotiRob: Companion robot Project,” RO-MAN 2007 – The 16th IEEE International Symposium on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, Jeju, Korea (South) (PDF). Jeju. pp. 919–924. doi:10.1109/ROMAN.2007.4415215.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Sojka, Petr; Horak, Aleš; Kopecek, Ivan (2008). Text, Speech and Dialogue: 11th International Conference, TSD 2008, Brno, Czech Republic, September 8-12, 2008, Proceedings. Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media. p. 551. ISBN 9783540873907.
- ^ “Lovot[らぼっと]”. Lovot. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ^ “Lovot[らぼっと]”. Lovot Emotional Robotics. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ^ Nagase, Youka (6 October 2020). “Japanese pet-robot Lovot is getting its own permanent cafe near Tokyo”. TimeOut. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ^ “NICOBO, a robot born out of empathy with consumers and sense of mission”. Panasonic. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ “Introducing NICOBO – Panasonic’s Smart but Vulnerable Companion”. Panasonic Global News. Panasonic. Retrieved 2 May 2023.
- ^ “Hyodol”. Hyodol. Panasonic. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “[MWC 24] S. Korean care robot company Hyodol wins health tech award at MWC”. AJUPRESS. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Jones, Raya A. (2019-09-01). “Concerning the Apperception of Robot-Assisted Childcare”. Philosophy & Technology. 32 (3): 445–456. doi:10.1007/s13347-018-0306-6. ISSN 2210-5441.
- ^ Bisconti Lucidi, Piercosma; Nardi, Daniele (2018-12-27). “Companion Robots: The Hallucinatory Danger of Human-Robot Interactions”. Proceedings of the 2018 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society. AIES ’18. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery. pp. 17–22. doi:10.1145/3278721.3278741. ISBN 978-1-4503-6012-8.