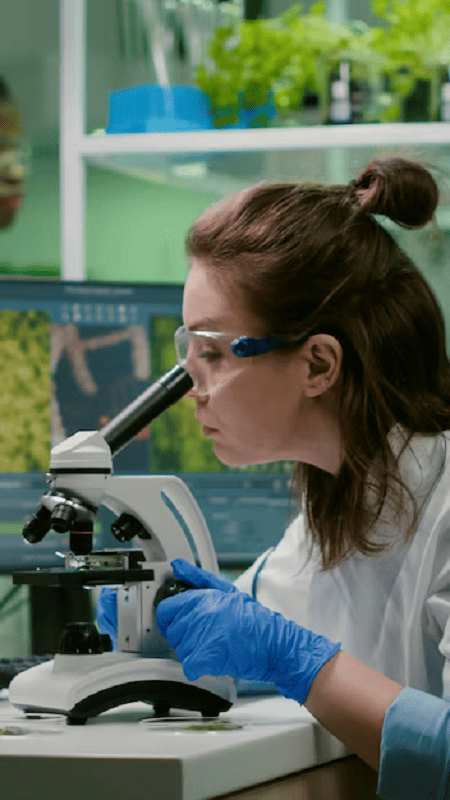
8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream
The development of 8K virtual reality (VR) headsets is an exciting trend that suggests VR technology will continue to evolve rapidly. While current VR headsets typically offer resolutions of 1080p to 4K, 8K VR headsets will bring ultra-high-definition visuals that improve immersion, offering sharper images and smoother experiences.
Here are some key factors driving the potential for 8K VR headsets to become mainstream:
1. Improved Visual Quality
8K resolution offers four times the pixels of 4K, allowing for incredibly detailed and sharp visuals. This is especially important in VR, where screen door effect (the visible grid between pixels) can break immersion. With 8K, this effect is significantly reduced, resulting in a more lifelike experience.
2. Hardware Advancements
The rapid progress in display and processing technologies, including better GPUs, faster processors, and specialized chips for VR, will make 8K headsets more accessible. Manufacturers like NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel are already working on chips powerful enough to handle such high resolutions.
3. Content Creation and Support
As more VR content is created with higher resolutions and more complex environments, 8K VR headsets will become more appealing. Game developers and filmmakers are beginning to design immersive experiences that will take full advantage of ultra-high-definition displays.
4. Decreasing Costs
As manufacturing processes improve and technology becomes more widespread, the cost of producing 8K displays and VR headsets will decrease. This will make the technology more affordable for consumers.
5. Enhanced Performance
With 8K resolution, the visual experience will be greatly enhanced, but this requires advancements in tracking, refresh rates, and latency control. Companies are already improving motion tracking and reducing lag to ensure smoother VR experiences, even at such high resolutions.
6. Virtual and Augmented Reality Integration
The line between virtual and augmented reality is becoming increasingly blurred, with both technologies benefiting from the rise of high-definition displays. In the future, 8K headsets could serve both VR and AR purposes, improving their utility in entertainment, training, and professional settings.
7. Consumer Demand for Immersive Experiences
As VR becomes more mainstream in gaming, entertainment, education, and even professional applications, users will demand increasingly immersive and visually impressive experiences. 8K headsets could be the next step in meeting those expectations.
While 8K VR headsets are not yet commonplace, ongoing technological advancements and market demand are making them more likely to become mainstream in the near future.
What is 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
The statement “8K Virtual Reality (VR) Headsets Will Become Mainstream” refers to the future trend in the development of virtual reality technology, specifically the rise of 8K resolution VR headsets becoming widely adopted by consumers and industries. Here’s a breakdown of what this means:
1. 8K Resolution in VR
- 8K resolution means a display with 7680×4320 pixels, which is four times the pixel density of 4K (3840×2160) and 16 times the resolution of 1080p (Full HD). In the context of VR, this ultra-high resolution will significantly enhance the clarity and sharpness of the virtual world, reducing visual artifacts like the screen door effect (where you see the grid of pixels between the image).
- High resolutions are crucial for immersion in VR because they allow for a more lifelike and realistic experience by providing more detailed and sharper visuals.
2. The Trend Towards Mainstream Adoption
- Mainstream adoption refers to the idea that, in the near future, 8K VR headsets will be affordable and accessible to a broad consumer base, much like current 4K or even 1080p VR headsets. This means that 8K VR headsets will be widely used for gaming, entertainment, education, professional applications, and more.
- The growing interest in immersive experiences, such as gaming, VR entertainment, and virtual tourism, is pushing demand for higher-quality VR headsets.
3. Technological Advancements
- As display technology (OLED, MicroLED, etc.), graphics processing units (GPUs), and processing power continue to improve, the feasibility of 8K VR becomes more practical.
- Companies like NVIDIA, AMD, and others are working on hardware capable of supporting such high resolutions in real-time applications like VR.
4. Content Creation and Support
- To take full advantage of 8K headsets, there will need to be more content (games, simulations, films) that supports 8K resolution. As VR content continues to evolve, developers will create experiences that can leverage the enhanced visual quality.
5. Improving Accessibility and Cost Reduction
- As the technology matures, the cost of production for high-resolution displays will decrease, making 8K VR headsets more affordable and accessible to consumers. In the early stages, such devices might be expensive, but eventually, mass production and wider adoption will lower costs.
6. Future Potential
- Beyond entertainment, 8K VR could have applications in fields like medicine, training, architecture, and education, where ultra-high-definition virtual environments can simulate real-world scenarios in extreme detail.
In short, “8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream” suggests that the future of VR headsets is heading towards ultra-high-resolution displays, offering significantly more immersive experiences, and will become common and affordable for regular consumers and various professional sectors.
Who is required 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
The statement “8K Virtual Reality (VR) Headsets Will Become Mainstream” suggests a trend in the VR industry, and it points to various groups and sectors that will benefit from and contribute to the adoption of 8K VR headsets becoming mainstream. Here’s who is likely to be required or impacted by the widespread adoption of 8K VR technology:
1. Consumers
- Gamers: As the demand for more immersive, realistic gaming experiences increases, gamers are likely to be a primary audience for 8K VR headsets. These users will demand sharper, more detailed visuals for gaming and virtual worlds.
- VR Enthusiasts and Early Adopters: People who are passionate about cutting-edge technology and VR experiences will be early adopters of 8K headsets.
- General Public: As the price of 8K VR headsets decreases, mainstream consumers interested in entertainment, virtual tourism, or social interactions in VR will also become part of the target audience.
2. Technology and Hardware Manufacturers
- Display Manufacturers: Companies involved in creating high-resolution displays, such as OLED or MicroLED, will need to innovate to produce large, high-quality displays suitable for VR applications at 8K resolution.
- VR Headset Companies: Companies like Oculus (Meta), HTC Vive, Sony, and Valve will need to develop VR headsets that support 8K resolution. This requires significant advancements in optics, display technologies, and ergonomic design to ensure comfort and performance.
- Graphics Card Manufacturers: Companies like NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel will need to produce graphics processing units (GPUs) capable of rendering high-quality 8K visuals in real-time, a huge challenge given the computational power required.
3. Content Creators and Developers
- Game Developers: As 8K VR headsets become more common, developers will be required to create VR games and experiences that take full advantage of 8K resolution, with richer detail, more realistic environments, and higher frame rates.
- Filmmakers and Animators: For virtual reality movies and simulations, filmmakers will need to create content at higher resolutions, requiring new techniques and rendering processes to achieve high visual quality at 8K.
- Educators and Trainers: VR is increasingly being used in training (e.g., medical, military, and technical fields), and these sectors will benefit from 8K VR for creating more detailed simulations.
4. Industries and Professionals
- Healthcare: Surgeons, doctors, and medical professionals may use 8K VR for surgical simulations or remote surgery applications, where high precision and clarity are critical.
- Architects and Designers: High-resolution VR can be used for more detailed design visualizations and architectural walkthroughs, offering a better experience when reviewing models and projects in virtual spaces.
- Military and Defense: The military could use 8K VR for training simulations, where realism and precision are crucial for tactics and scenarios.
- Entertainment and Virtual Tourism: The entertainment industry could see an increase in virtual concerts, live events, and immersive virtual tourism, requiring 8K VR headsets to deliver an incredibly realistic experience.
5. Tech Enthusiasts and Influencers
- Tech Journalists and Reviewers: As 8K VR headsets enter the market, tech reviewers and influencers will play a key role in shaping public perception and demand for these devices.
- Developers and Innovators: Those at the forefront of virtual reality innovation, including researchers and developers working on the next generation of VR experiences, will be required to optimize applications for 8K technology.
6. Governments and Educational Institutions
- Educational Institutions: Schools and universities might adopt 8K VR for educational purposes, using highly immersive virtual classrooms and simulations to teach complex subjects or to provide hands-on experiences in fields like science, history, and medicine.
- Government Agencies: Governments might use 8K VR for training simulations, urban planning, and even virtual city tours for citizen engagement.
7. Investors and Businesses
- Investors: Companies and investors in the tech industry are likely to push for the development and adoption of 8K VR, seeing the potential for growth in VR hardware and software markets.
- Content Providers and VR Platforms: Platforms that deliver VR content, such as SteamVR, Oculus Store, or PlayStation VR, will need to support high-resolution content, driving demand for 8K content creation.
In conclusion, the adoption of 8K VR headsets will impact a wide range of groups, including consumers, tech companies, content creators, industries such as healthcare and education, and professionals across various fields. Everyone from early adopters to industries seeking detailed simulations and entertainment experiences will benefit as 8K VR becomes more mainstream.
When is required 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
The timeline for when 8K Virtual Reality (VR) headsets will become mainstream is still uncertain, but it is influenced by several factors, including technological advancements, market demand, content creation, and cost reduction. Here are some key points to consider:
1. Technological Advancements
- Display and GPU Development: The technology for producing high-quality 8K displays and the necessary graphics processing units (GPUs) to support such high resolutions is progressing steadily. However, creating VR headsets with 8K resolution requires substantial advancements in both optics (to ensure clarity and prevent motion sickness) and processing power (to maintain smooth performance at high frame rates). These developments may take a few more years to become widely available.
- Processing Power: Achieving real-time rendering for 8K in VR is resource-intensive, requiring the latest GPUs and processors. As companies like NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel continue to improve the hardware, we can expect better performance for 8K VR. This could be more feasible within the next 3-5 years.
2. Cost Reduction
- Early versions of 8K VR headsets will likely be expensive due to the complexity of the technology. However, like other technology trends, the cost of manufacturing 8K displays and associated hardware will decrease as production scales up. This could happen within 5-7 years, making 8K VR headsets more affordable for mainstream consumers.
- For example, OLED and MicroLED display prices have dropped significantly over the years, and the same is expected for 8K VR displays as the technology matures.
3. Content Creation and Adoption
- For 8K VR to become mainstream, there must be enough content—such as games, movies, educational experiences, and training simulations—that supports 8K resolution. Content creators will need to build experiences that leverage the increased resolution. This could take several years, depending on how quickly industries like gaming, film, and training adopt 8K for VR experiences.
- We may see this shift starting within 3-5 years as VR platforms push for higher-quality content.
4. Industry and Consumer Demand
- Consumer demand for immersive experiences is already growing in gaming and entertainment. As VR usage increases in these areas, there will be a push for higher resolution headsets to match the growing need for realism. However, it will take time for this demand to reach the scale required for mass adoption.
- If trends continue, 8K VR headsets could start gaining mainstream traction within 5-7 years, with broader adoption taking place in 7-10 years as they become more affordable.
5. Current Predictions
- Short-Term (3-5 years): We may see high-end 8K VR headsets emerging for enthusiasts and early adopters. These headsets could be expensive and targeted at professional users in fields like healthcare, architecture, and training.
- Medium-Term (5-7 years): 8K VR headsets may become more common in gaming and entertainment, with prices dropping enough for general consumers. By this time, manufacturers will likely have addressed issues like comfort, refresh rate, and motion sickness.
- Long-Term (7-10 years): As the technology matures, 8K VR headsets could become mainstream, with widespread adoption in both consumer markets and professional sectors like education, medicine, and design.
In conclusion, while the technology for 8K VR is advancing, mainstream adoption is likely to occur within 5-10 years. This timeline depends on continued improvements in hardware, content creation, and the reduction of costs that will make 8K VR headsets accessible to a wider audience.
Where is required 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
The widespread adoption of 8K Virtual Reality (VR) headsets will likely take place across several regions and industries, depending on technological infrastructure, market demand, and innovation. Here are the key places and sectors where 8K VR headsets are expected to become mainstream:
1. Geographical Regions
- United States: The U.S. is a global leader in technology innovation and has a large consumer base for gaming, entertainment, and professional VR applications. Major tech companies like Meta (Oculus), Sony, Valve, and HTC are based here, and the country is home to a growing VR industry. The U.S. will likely see an early adoption of 8K VR for gaming, entertainment, and professional sectors (e.g., healthcare, education, and training).
- Europe: Europe is also home to strong VR research and development hubs, particularly in countries like Germany, the UK, and France. The region is involved in several VR-related projects in fields such as education, medicine, manufacturing, and design. High-quality VR content creation is strong in Europe, and 8K VR headsets may see adoption for industrial and academic purposes, as well as in entertainment.
- Asia:
- Japan: Japan is a pioneer in gaming, electronics, and robotics, so it is likely to be a key market for 8K VR adoption. Sony, for instance, is actively involved in VR development with its PlayStation VR platform, and Japan has seen significant interest in VR gaming and entertainment experiences.
- China: With its rapidly growing tech market and strong investment in VR, China is another significant market for 8K VR adoption. The demand for VR gaming, entertainment, and education is high, and the country has many tech companies driving advancements in VR hardware and content creation.
- South Korea: South Korea, with its high-speed internet infrastructure and strong gaming culture, will likely be an early adopter of 8K VR, especially for gaming and virtual social experiences.
2. Industries and Sectors
- Entertainment and Gaming:
- The entertainment industry is one of the most likely sectors where 8K VR headsets will become mainstream. Companies involved in gaming, film, and VR experiences will push for higher resolution and more immersive experiences, especially for gaming, virtual concerts, immersive movies, and live events. These experiences will likely be popular in gaming hubs like the U.S., Japan, South Korea, and parts of Europe.
- The gaming industry will drive much of the demand for 8K VR headsets as immersive gaming experiences become more realistic and demanding in terms of graphical fidelity.
- Education and Training:
- Medical and Surgical Training: 8K VR headsets will be used in medical fields for surgical simulations and medical training where high visual fidelity is crucial for accuracy. Hospitals, universities, and research centers globally, particularly in advanced economies like the U.S., Germany, and Japan, will adopt this technology.
- Military Training: Countries with significant military budgets, such as the U.S., Russia, China, and India, will use 8K VR for realistic training simulations.
- Corporate and Vocational Training: Businesses in sectors like aerospace, automotive, manufacturing, and engineering will also use 8K VR for detailed training simulations. Regions with a strong industrial base, like Germany, South Korea, and parts of the U.S., will be major adopters.
- Healthcare:
- The healthcare sector will adopt 8K VR for virtual consultations, diagnostic simulations, physical therapy, and medical research. This will be particularly relevant in advanced healthcare systems in the U.S., Europe, Japan, and China, where technology adoption tends to be quicker.
- Architecture and Design:
- Architects and designers will use 8K VR for more detailed and realistic virtual walkthroughs of buildings and products. Regions with strong architectural industries, like the U.S., Germany, and the Middle East (e.g., the UAE), will be early adopters.
- Real Estate: 8K VR will allow for virtual property tours and real estate visualizations, becoming mainstream in major cities worldwide.
3. Consumer Electronics and VR Companies
- Silicon Valley (USA): As the hub of tech innovation, companies like Meta (Oculus), Sony, Valve, and others will lead the development and distribution of 8K VR headsets. The U.S. is likely to be one of the earliest markets for these devices.
- China and South Korea: Major electronics manufacturers like Samsung and LG are based in these regions and will play a role in producing the high-resolution displays needed for 8K VR. These regions also have thriving VR ecosystems, especially in gaming and entertainment.
- Europe: Companies like HTC Vive (Taiwan-based but with significant operations in Europe) and European VR startups will contribute to the adoption of 8K VR in professional and consumer markets.
4. Virtual Reality Platforms and Software Providers
- SteamVR, Oculus Store, PlayStation VR, and other VR content platforms will provide 8K-capable content. These platforms will be instrumental in making 8K VR headsets mainstream by offering content optimized for high-resolution displays.
5. Public and Private Sector Adoption
- Governments and Educational Institutions: Countries with advanced education systems and strong public-private partnerships, like those in the U.S., Germany, Canada, and the UK, will adopt 8K VR for virtual classrooms, training programs, and public services.
- Corporate Adoption: Large corporations across industries like automotive, aviation, engineering, and finance will use 8K VR for virtual collaboration, prototyping, and training.
In Summary:
- 8K VR headsets are likely to become mainstream in high-tech markets like the U.S., Europe, Japan, South Korea, and China.
- They will first be adopted by early adopters and specialized industries such as gaming, entertainment, medical training, and architecture.
- As the technology matures and becomes more affordable, consumer markets across the globe will gradually adopt 8K VR, especially in regions with strong tech infrastructure and innovation ecosystems.
The overall adoption will vary by region and sector, but the major markets for 8K VR are expected to be in North America, Europe, and Asia, with increasing applications across industries.

How is required 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
The process of 8K Virtual Reality (VR) headsets becoming mainstream will require significant advancements and improvements in several key areas. Here’s a breakdown of how this transition could happen:
1. Technological Advancements
- Display Technology:
- 8K Resolution Displays: The primary requirement for 8K VR headsets is the development of high-quality 8K displays that are compact and can be used in VR headsets. These displays must provide exceptional visual clarity, pixel density, and color accuracy to deliver immersive experiences.
- Low Latency and High Refresh Rates: For VR, low latency (minimal delay between the user’s action and the display’s response) and high refresh rates (at least 90Hz or higher) are essential to ensure a smooth, comfortable experience and reduce motion sickness. To support 8K resolution, the display must handle a high amount of data while maintaining these low-latency and high-refresh-rate requirements.
- Graphics Processing Units (GPUs):
- The hardware required to support 8K VR, particularly in terms of GPUs, needs to be extremely powerful to handle real-time rendering at 8K resolution. Companies like NVIDIA and AMD are already working on GPUs capable of supporting higher resolutions, but these need to be further optimized for VR.
- The hardware must also ensure that the rendering occurs at a high frame rate (around 90-120 FPS) to create a smooth and immersive experience.
- Optics and Lens Improvements:
- The optics (lenses) in the VR headset need to be of high quality to minimize distortions and ensure clarity at 8K resolution. Advanced lenses will also be required to prevent issues like screen door effect (visible pixel gaps) and to provide a wide field of view (FOV).
- Battery Life and Power Efficiency:
- 8K VR headsets will be power-hungry, which could limit their battery life. As a result, improvements in battery technology and power efficiency are needed to make these headsets practical for extended use. Developing batteries that can last for hours while delivering the necessary power is critical for adoption.
2. Content Creation and Availability
- 8K Content: One of the significant factors for mainstream adoption of 8K VR is the availability of high-quality content that justifies the need for 8K resolution. Content creators in industries such as gaming, cinema, training simulations, and education must produce content that takes advantage of the increased resolution.
- For example, VR gaming will require new game engines and assets designed for 8K resolution.
- Movies and VR experiences will also need to be filmed and rendered in 8K, which involves heavy investments in production and post-production.
- Content Delivery Platforms: Streaming platforms and content providers (like Oculus, PlayStation VR, SteamVR) will need to support 8K VR content. They must also ensure that the infrastructure, such as bandwidth and data delivery, is robust enough to handle the massive data required for 8K VR content without causing delays or buffering.
3. Cost Reduction and Affordability
- Economies of Scale: As the demand for 8K VR headsets grows, economies of scale will help reduce the production cost of the hardware. Manufacturing advancements and increased competition will lower the cost of displays, processors, and optics.
- Affordable Pricing: Initially, 8K VR headsets will be targeted at enthusiasts and professionals. However, for the technology to become mainstream, prices need to drop significantly. The market will have to see a shift from premium pricing to affordable models, potentially in the range of $500-$1000 for high-end consumer devices. This could take 5-7 years, depending on market dynamics.
4. Enhanced User Experience
- Comfort and Ergonomics: VR headsets, particularly high-resolution ones like 8K, need to be comfortable for extended use. Current VR headsets sometimes suffer from being too bulky or heavy, leading to discomfort. Future 8K VR headsets will need to be lightweight, well-balanced, and easy to adjust, with advanced comfort features like cooling systems and better facial interfaces.
- Accessibility and Ease of Use: To appeal to a broader audience, 8K VR headsets should be easy to set up and use. This includes minimizing cables, offering wireless options, and providing intuitive software for ease of navigation.
- Wireless Technology: Wireless 8K VR headsets would require strong wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 7, to transmit the large amount of data required for 8K video without latency or compression. This would remove the need for heavy cables, making VR more comfortable and portable.
5. Market Demand and Consumer Adoption
- Increased VR Usage: As VR adoption continues to grow in various sectors such as gaming, healthcare, education, and training, there will be more demand for higher-quality experiences. This increased demand will drive the adoption of 8K VR as consumers and businesses push for more immersive and realistic visuals.
- Gaming and Entertainment: The gaming and entertainment sectors are likely to be the first major drivers of 8K VR. As consumers seek more lifelike and immersive experiences, 8K VR could become the new standard for next-gen gaming and entertainment experiences like virtual tourism, concerts, and interactive cinema.
6. Regulatory and Industry Standards
- Industry Certification and Standardization: For 8K VR to become mainstream, there needs to be standardization in terms of hardware and content. This includes agreements on frame rates, resolution, and compatibility between different VR systems and content platforms. Industry standards will also ensure that the VR content works across different headsets and devices.
7. Marketing and Education
- Consumer Awareness: The public will need to be educated on the benefits of 8K VR over lower-resolution alternatives. As consumers understand the improvements in immersion, realism, and gaming quality, demand will increase.
- Marketing Strategies: Manufacturers will need to launch effective marketing campaigns to showcase the potential of 8K VR, not only for gaming but also for professional uses such as training, design, medical applications, and virtual collaboration.
In Summary:
For 8K Virtual Reality headsets to become mainstream, several key factors must align:
- Technological breakthroughs in display, GPU, and battery technologies.
- Content creation that takes advantage of 8K resolution.
- Lower prices due to economies of scale and market competition.
- Enhanced user experience in terms of comfort and ease of use.
- Increased market demand driven by gaming, entertainment, and professional sectors.
- Industry standards to ensure compatibility and interoperability.
- Effective marketing and consumer education to drive adoption.
This transition is likely to take 5-10 years as the technology matures, content becomes more available, and costs come down, ultimately making 8K VR accessible to a broader audience.
Case study is 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
Case Study: 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Becoming Mainstream
Introduction
The concept of 8K Virtual Reality (VR) headsets becoming mainstream is an exciting possibility for the future of immersive technology. With technological advancements, a growing demand for high-quality immersive experiences, and the continued development of VR content, 8K VR could redefine industries like gaming, entertainment, training, and healthcare. This case study explores the potential transition of 8K VR headsets from niche, high-end devices to accessible, mainstream products, addressing the key factors, challenges, and implications for various sectors.
Background
VR headsets have evolved over the past decade from simple gaming devices to complex platforms for professional applications, education, and entertainment. While current VR headsets like the Oculus Quest 2 and PlayStation VR 2 offer 4K resolution, the leap to 8K VR offers significant improvements in image clarity, immersion, and user experience. The integration of 8K resolution into VR headsets holds promise, but it also comes with challenges, including the demand for better hardware, content creation, and consumer adoption.
Key Factors Influencing the Mainstream Adoption of 8K VR
- Technological Advancements:
- Display Technology: The key to 8K VR headsets is the ability to produce high-resolution, compact displays. Companies like Samsung and LG are developing OLED and microLED panels that could meet the demands of 8K resolution at the small form factor required for VR headsets.
- Graphics Processing Units (GPUs): As 8K resolution requires significant computational power, the development of GPUs capable of supporting high-frame-rate 8K rendering is critical. NVIDIA and AMD are already releasing GPUs that are designed to handle next-gen gaming and VR, but these technologies need to be further optimized for VR headsets.
- Latency and Refresh Rate: A smooth VR experience requires a low latency and a high refresh rate (minimum 90Hz). VR headsets with 8K resolution will need to meet these specifications without inducing motion sickness, which requires advances in both display and processing power.
- Content Availability:
- For 8K VR to gain traction, there must be high-quality content available. This includes VR games, 360-degree video experiences, and virtual simulations.
- As of now, 8K content creation is limited due to the high cost and complexity involved. However, the growth of 5G networks, which can support the data bandwidth required for 8K content streaming, combined with cloud computing and rendering services, could accelerate the availability of 8K VR content.
- Affordability:
- The primary barrier to the mainstream adoption of 8K VR headsets is cost. Early models of 8K VR are expected to be expensive due to the high-end components required for the display, GPU, and processing.
- Over time, as technology becomes more refined and mass production scales, costs should decrease. Consumer-grade VR headsets with 8K resolution may eventually become as affordable as current 4K models, which will drive wider adoption.
- User Experience and Comfort:
- VR adoption has faced challenges related to comfort and user experience. Early VR systems were criticized for being too heavy, bulky, or uncomfortable for extended use.
- 8K VR headsets will need to be significantly lighter and more ergonomic, with better ventilation and adjustable head straps to ensure comfort during long sessions.
- Advances in wireless technology (like Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 7) will also play a crucial role in improving user experience by eliminating cumbersome wires and cables.
Timeline for Mainstream Adoption
The transition to 8K VR becoming mainstream is not expected to happen overnight. The market adoption curve typically follows these stages:
- Innovators and Early Adopters (1-3 years):
- Initially, 8K VR will target enthusiasts and professional users. High-end models will be released by companies like HTC Vive, Oculus, and Sony, which will cater to those willing to pay a premium for the latest in VR technology.
- Corporate training, medical applications, and professional gaming will likely be the first sectors to adopt 8K VR, where the need for precision and high-quality visuals is paramount.
- Early Majority (3-7 years):
- As technology improves and prices drop, 8K VR headsets will become more accessible to the broader public. This will coincide with better content availability, including both entertainment and educational applications.
- The growth of VR arcades, fitness programs, and virtual tourism will further drive adoption in the entertainment and lifestyle sectors.
- Key events like E3 (Electronic Entertainment Expo) and CES (Consumer Electronics Show) will showcase advancements in 8K VR, pushing the technology to the forefront of mainstream discussions.
- Late Majority (7+ years):
- By this stage, 8K VR headsets could become standard consumer products, akin to the transition from HD to 4K televisions. Prices will have significantly dropped, and the content ecosystem will have matured with a steady supply of native 8K VR content across various platforms.
- The potential for 8K VR to revolutionize industries like healthcare, education, remote work, and gaming will be fully realized as businesses and consumers integrate this technology into their daily lives.
Case Study Example: The Role of Gaming and Entertainment in Driving 8K VR
Background: The gaming industry has been one of the primary drivers of VR adoption, and it is expected to be a major player in the transition to 8K VR. As gamers increasingly demand more immersive and realistic experiences, the demand for higher resolution and better visuals will push hardware and content developers to adopt 8K.
Key Players:
- Oculus (Meta): The Oculus Quest and Quest 2 have gained significant market share in the VR space. Meta is expected to push further into 8K VR, with rumors of future headsets that could support 8K or even 16K resolution.
- Sony: With the PlayStation VR2, Sony is already setting the stage for high-quality VR experiences. They are likely to be a major player in 8K VR, especially with the release of new consoles and VR technologies.
Impact on the Industry:
- The introduction of 8K VR gaming will drive content creation in gaming engines such as Unreal Engine and Unity, which are already capable of supporting high-resolution textures and environments.
- Game developers will focus on creating titles that can leverage the power of 8K VR, offering experiences that are more immersive, realistic, and responsive.
- Streaming platforms like Twitch and YouTube will evolve to support 8K streams, enabling content creators to broadcast in ultra-high resolution.
Conclusion
8K VR headsets becoming mainstream is an exciting possibility but will require a concerted effort across multiple industries. Technological advancements in display and GPU performance, coupled with content creation and affordability improvements, will play key roles in this transition. Gaming and entertainment, along with applications in professional and educational sectors, will drive the adoption of 8K VR. While it may take 5-10 years for the technology to become widespread, the increasing demand for higher-quality immersive experiences will ensure that 8K VR is not just a niche product but a standard for future VR applications.
White paper on is 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
White Paper: Will 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Become Mainstream?
Executive Summary
8K Virtual Reality (VR) headsets represent the cutting edge of immersive technology, offering a new frontier in visual clarity and user experience. With advancements in display technology, processing power, and wireless communication, the potential for 8K VR to become mainstream is becoming increasingly realistic. However, while the vision for ultra-high-definition VR is enticing, the path to mainstream adoption is complex, involving technical, economic, and content-related challenges. This white paper explores the viability of 8K VR becoming mainstream, analyzing the key drivers, barriers, and market trends that will shape its widespread adoption.
Introduction
Virtual Reality has transformed the way we interact with digital environments, from immersive gaming and entertainment to professional training and healthcare. However, despite its rapid growth, current VR headsets still face limitations in resolution, image quality, and overall immersion. With 4K VR headsets becoming more common, the next leap in visual fidelity is 8K resolution — offering sharper images, higher clarity, and enhanced realism. The adoption of 8K VR in the consumer market, however, is contingent upon several factors, including advances in hardware, content development, and pricing strategies.
This paper outlines the key factors influencing the adoption of 8K VR headsets, identifies potential market drivers, and presents a comprehensive timeline for mainstream integration.
Technological Advancements Driving 8K VR Adoption
- Display Technology: The display is one of the most critical components of any VR headset. The current generation of VR headsets uses 4K displays (2K per eye). However, achieving 8K VR (4K per eye) requires the development of ultra-high-definition displays that are both compact and capable of high refresh rates. Technologies such as OLED and MicroLED are expected to be key enablers of 8K resolution. These displays provide deep contrast and high color accuracy, essential for creating a lifelike, immersive experience.
- Graphics Processing Power: The next challenge in the adoption of 8K VR is the processing power required to handle the high bandwidth and pixel density of 8K video. Graphics processing units (GPUs) from companies like NVIDIA and AMD are evolving rapidly, with products like the RTX 4090 and AMD Radeon 7900 XTX capable of supporting 8K gaming at higher frame rates. However, rendering 8K VR content smoothly, while maintaining low latency and high refresh rates (e.g., 90Hz or higher), requires significant computational power, which must be balanced with the cost and power efficiency.
- Wireless Technology: 8K VR requires high-bandwidth wireless connections for seamless performance. Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 7 are expected to play a vital role in enabling wireless 8K streaming. These technologies provide higher data transfer rates (up to 10 Gbps), ensuring that VR data can be transmitted without lag or disruption, a critical aspect for a smooth and immersive experience.
- Latency and Frame Rate: One of the core challenges for VR headsets is achieving low latency and high refresh rates to avoid motion sickness and discomfort. The target for 8K VR is to maintain sub-20ms latency while supporting high refresh rates (90Hz or more). This ensures that users experience a seamless interaction with the virtual environment without motion blur or delay.
Key Drivers of 8K VR Adoption
- Gaming and Entertainment: Gaming is arguably the most influential driver of VR technology. As gamers demand increasingly realistic and immersive experiences, the push for higher resolution and better visual fidelity will be a key factor in the shift toward 8K VR. Additionally, the entertainment industry is adopting VR for virtual concerts, 360-degree films, and immersive storytelling experiences. The combination of these factors is likely to accelerate the push toward 8K VR as a mainstream product.
- Healthcare and Education: In fields like medical imaging and surgical training, the need for high-resolution, precise visual feedback makes 8K VR a compelling choice. Similarly, immersive educational simulations could benefit from the enhanced realism provided by 8K resolution, offering more detailed and lifelike environments for both professional training and personal learning.
- Virtual Work and Remote Collaboration: With the rise of remote work, VR is increasingly being considered for creating virtual meeting spaces and collaborative environments. As 8K VR technology becomes more accessible, businesses may adopt it for creating highly detailed and interactive meeting rooms, facilitating more effective and realistic remote collaboration.
- Consumer Demand for High-Definition Content: The general consumer market is already familiar with high-definition media, with the transition from HD to 4K now widely complete in television and entertainment. As 8K televisions gain popularity, there is growing consumer awareness of the benefits of ultra-high-definition content. This trend will extend to VR, especially as 8K content creation tools become more widely available.
Challenges to Overcome
- Cost: The most significant barrier to the mainstream adoption of 8K VR headsets is cost. Current VR headsets with 4K displays are already priced at a premium, and the development of 8K-ready hardware (displays, GPUs, wireless components) will inevitably increase prices further. Early models are likely to remain prohibitively expensive for the average consumer, with prices expected to fall over time as production scales and technology matures.
- Content Creation: The development of native 8K VR content is a significant hurdle. Producing immersive VR experiences in 8K resolution requires substantial resources and expertise. Furthermore, the data size for 8K content is immense, which may complicate content streaming and storage solutions. However, as cloud rendering and AI-based upscaling technologies improve, the barrier to entry for content creators will gradually decrease.
- Hardware Limitations: VR headsets need to be lightweight, comfortable, and capable of operating for extended periods without overheating. The addition of 8K resolution may increase the weight and complexity of the device. Manufacturers must find ways to integrate high-end displays and processing power while maintaining a user-friendly form factor.
- Connectivity Infrastructure: The demand for high-bandwidth connectivity required to stream 8K content could be hindered by current internet infrastructure. Although 5G and Wi-Fi 6 are improving network capabilities, rural and remote areas may face challenges in accessing the required bandwidth to experience 8K VR.
Market Outlook and Timeline
The timeline for mainstream adoption of 8K VR headsets will depend on several factors:
- Early Adoption (1-3 years): The first 8K VR headsets will likely target enthusiasts, gamers, and professional users. These devices will be costly and feature advanced specifications tailored to high-end applications, such as medical training, military simulations, and immersive entertainment.
- Mainstream Adoption (3-7 years): As costs decrease and technology improves, 8K VR headsets will become more affordable and accessible to the general consumer market. Content creation will also become more widespread, with platforms such as YouTube, Twitch, and Netflix potentially supporting 8K VR content. The increasing availability of 8K VR games, movies, and educational tools will further drive adoption.
- Mass Adoption (7+ years): By the end of the decade, 8K VR could become a standard feature for gaming consoles, smartphones, and personal entertainment systems. As wireless bandwidth improves and content platforms evolve, 8K VR headsets may be ubiquitous in everyday life, transforming the way we work, learn, and interact with digital environments.
Conclusion
While the mainstream adoption of 8K VR headsets is not immediate, it is an inevitable progression of the immersive technology landscape. Driven by advancements in display technologies, graphics processing, and content creation, 8K VR is poised to revolutionize several industries, from entertainment to healthcare. As the cost of hardware decreases and consumer demand for high-definition experiences grows, 8K VR will likely become a key player in the future of digital interaction. However, overcoming the technical, economic, and content-related challenges will require concerted efforts from manufacturers, developers, and content creators over the next decade.
Industrial Application of is 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
Industrial Applications of 8K Virtual Reality Headsets
As 8K virtual reality (VR) headsets become more accessible and sophisticated, they are expected to have significant applications across various industries. The immersive, high-definition experience offered by 8K VR will elevate current practices, providing innovative solutions for training, design, maintenance, simulation, and communication. Below are the key industrial sectors where 8K VR will likely have a profound impact:
1. Manufacturing and Industrial Design
Product Design and Prototyping
- 8K VR enables engineers and designers to create and interact with highly detailed virtual prototypes of products. This level of detail (8K resolution) allows for accurate visualization of materials, textures, and dimensions before physical prototypes are created.
- VR modeling tools like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) can be integrated into immersive VR environments, providing teams with a new way to refine product designs, test ergonomics, and conduct virtual assembly simulations, all in hyper-realistic detail.
Virtual Assembly Lines and Factory Floor Simulation
- Simulation of manufacturing processes and factory layouts becomes more realistic in 8K VR, aiding companies in optimizing production workflows, improving safety protocols, and designing better facilities.
- Training factory workers in the safe operation of complex machinery using virtual assembly lines can be more effective and cost-efficient with highly detailed VR environments, minimizing downtime and reducing risks associated with traditional training.
2. Healthcare and Medical Training
Surgical Training and Planning
- In the medical field, 8K VR can be transformative for surgical training. The ultra-high resolution allows trainees to examine human anatomy in detail, improving their ability to understand complex surgical procedures.
- Surgeons can practice in a virtual operating room, refining techniques without the risk of actual patients. 8K VR can offer accurate 3D visualizations of organs, tissues, and bones, enabling better pre-surgical planning and decision-making.
Remote Consultations and Telemedicine
- 8K VR could be used to conduct remote medical consultations. By providing lifelike virtual consultations, doctors and specialists can work with patients or other healthcare professionals across the globe, creating more precise diagnoses and treatment plans.
- Telemedicine could be enhanced through virtual environments, enabling detailed medical imaging and real-time collaboration between healthcare providers, improving patient outcomes.
3. Education and Professional Training
Immersive Learning Environments
- 8K VR can bring textbooks and theoretical lessons to life by providing immersive, interactive learning experiences. Students can visit historical landmarks, explore microscopic biology, or interact with scientific phenomena as if they were physically present.
- In fields like engineering, architecture, and medicine, the detailed visual experience offered by 8K VR aids in explaining complex concepts and procedures that might be difficult to comprehend through traditional methods.
Corporate and Technical Training
- Industries like automotive, aerospace, and construction can use 8K VR for technical training simulations. For instance, workers can practice troubleshooting machinery, navigating hazardous environments, or performing maintenance on expensive equipment in a virtual world.
- Realistic 8K VR environments help trainees gain hands-on experience in a safe, controlled setting, reducing errors during actual operations and increasing safety standards.
4. Aerospace and Defense
Simulation and Training for Pilots and Soldiers
- 8K VR offers exceptional potential in military and aviation training by providing extremely realistic flight and combat simulations. For instance, pilot training can be enhanced by simulating different weather conditions, technical failures, and emergency scenarios with high visual fidelity.
- For soldiers, immersive VR training allows them to practice complex battlefield strategies or navigate unfamiliar terrain in environments that mimic real-world conditions, all rendered in stunning detail.
Design and Testing of Aircraft
- Engineers can use 8K VR to visualize aircraft designs at an intricate level, evaluating performance under different conditions and testing potential improvements. By immersing themselves in realistic virtual environments, engineers can analyze designs more effectively than through traditional methods.
5. Real Estate and Urban Planning
Architectural Visualization and Design
- Architects and urban planners can use 8K VR to showcase architectural designs in an immersive environment, allowing clients to walk through virtual buildings and spaces before construction begins. The high-resolution visuals provide a more accurate representation of how a building or urban development will look and feel.
- Virtual real estate tours can be enhanced, offering potential buyers a detailed and immersive look at properties from the comfort of their homes, potentially accelerating decision-making and reducing the need for physical visits.
Urban Simulations and Environmental Impact Analysis
- Urban planners can simulate entire cities in 8K resolution, allowing them to analyze the impact of infrastructure projects, such as new transportation systems, residential areas, or commercial developments, on the environment and urban dynamics.
- With this level of detail, planners can identify potential challenges (traffic congestion, pollution, etc.) and improve their designs accordingly.
6. Entertainment and Media
Virtual Cinemas and Live Events
- The entertainment industry stands to benefit significantly from 8K VR, offering an entirely new form of virtual cinema. Filmmakers can create highly detailed, immersive environments for viewers to experience films and shows in ways that traditional cinema cannot replicate.
- Live events such as concerts, sports games, and theatrical performances can also be streamed in 8K VR, allowing viewers to attend in virtual arenas or theaters with hyper-realistic detail, providing them with a much more immersive experience than current HD or 4K VR options.
Gaming
- 8K VR is expected to be a game-changer for the gaming industry, where players can experience unprecedented levels of detail and immersion. In 8K VR gaming, players will feel completely surrounded by stunningly lifelike environments, enhancing their overall sense of presence and realism in the game world.
7. Automotive Industry
Virtual Showrooms and Test Drives
- Car manufacturers can create virtual showrooms where potential buyers can experience every aspect of a car in 8K VR, from interior details to the feel of the vehicle’s performance. This level of detail can help consumers make more informed purchasing decisions without having to visit a physical dealership.
- Virtual test drives in a hyper-realistic setting will allow customers to experience how the car handles in various driving conditions, offering an immersive pre-purchase experience.
Design and Engineering
- Automotive engineers can use 8K VR to simulate the design and crash testing of vehicles, improving both safety features and design aesthetics. This allows for faster iterations in product development, with engineers making data-driven decisions based on detailed simulations.
Conclusion
8K Virtual Reality headsets have the potential to revolutionize industries by providing highly detailed, immersive, and interactive experiences. From product design and medical training to military simulations and entertainment, the applications are vast. However, the widespread adoption of 8K VR in these sectors will depend on overcoming technical challenges such as cost, content creation, and hardware limitations.
As technology continues to improve and the cost of production decreases, we can expect 8K VR to become a powerful tool in industries that rely on precision, immersion, and interactivity, marking the beginning of a new era in industrial applications.
Research and Development is 8K Virtual Reality Headsets Will Become Mainstream ?
Research and Development in 8K Virtual Reality Headsets
The development of 8K virtual reality (VR) headsets is an emerging frontier in immersive technology, with numerous research and development (R&D) efforts underway to address technical challenges, enhance user experiences, and unlock new industrial applications. As the demand for ultra-high-resolution VR experiences increases, R&D activities are focused on improving the hardware, software, content creation, and user interaction. Below is an overview of key areas in R&D related to the mainstream adoption of 8K VR headsets:
1. Display Technology: Pushing the Boundaries of Resolution
High-Resolution Displays
- 8K resolution (7680 × 4320 pixels) requires substantial advancements in display technology, particularly in terms of pixel density, contrast ratios, and color accuracy. Researchers are focused on developing OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diodes), microLED, and LCD panels that can support this resolution while maintaining high refresh rates and wide viewing angles.
- Low latency and high frame rates are essential for maintaining the smoothness of VR experiences. Display developers are working on optimizing high-refresh-rate panels (120 Hz or higher) to prevent motion sickness and ensure a fluid, immersive experience.
Foveated Rendering Technology
- To alleviate the immense computing power needed for 8K VR, foveated rendering is a major focus. This technology focuses rendering power on the area where the user’s eyes are looking (the fovea) and reduces resolution in peripheral areas. R&D in eye-tracking systems and advanced algorithms will play a critical role in improving this technology, enabling 8K resolution experiences while conserving processing resources.
2. Processing Power and Graphics Rendering
Advanced GPU and Processor Design
- 8K VR headsets demand substantial graphics processing power to handle the rendering of ultra-high-definition environments. The development of new graphics processing units (GPUs), system-on-chip (SoC) designs, and specialized VR processors is a key area of research to meet the heavy computational demands of 8K VR content.
- Companies like NVIDIA and AMD are at the forefront of GPU development, working on high-performance chips that can render 8K content at high frame rates (such as 240 Hz or more) without sacrificing performance or creating latency.
- Parallel processing and cloud-based rendering may also play a role in the R&D for 8K VR, enabling VR content to be rendered off-site and streamed to users with minimal hardware requirements.
Compression Algorithms
- Streaming 8K content requires efficient data compression algorithms that preserve image quality without causing excessive delays. R&D into high-efficiency video coding (HEVC) or newer codecs like VVC (Versatile Video Coding) aims to reduce the bandwidth needed for 8K video streaming, making it feasible to deliver high-quality VR experiences over standard internet connections.
3. Optics and Visual Fidelity
Improved Lens Systems
- To achieve optimal viewing in VR headsets, lens systems must be designed to handle the increased resolution of 8K content without distortion or blurring. Research is focused on creating custom-designed lenses that can accurately project ultra-high-definition images from the display to the user’s eyes while preventing issues like screen-door effect or chromatic aberrations.
- Aspheric lenses and varifocal optics are being studied to offer clearer images, reduce eye strain, and provide a more natural and comfortable VR experience for users over extended periods.
Field of View (FOV) Enhancements
- A key aspect of the 8K VR experience is achieving a broad field of view (FOV) that enhances immersion. Researchers are working on increasing the FOV in VR headsets without sacrificing image quality. Currently, most VR headsets offer an FOV of around 100 to 120 degrees, but the next-generation headsets targeting 8K VR will likely push this further, aiming for more natural, panoramic views.
4. User Interaction and Immersion
Haptic Feedback and Sensory Integration
- To make the 8K VR experience even more immersive, there is significant R&D into haptic feedback technology that allows users to feel virtual environments. Research is focused on enhancing haptic gloves, bodysuits, and controllers to provide realistic sensations (like touch, temperature, and texture) that match the visual fidelity of 8K VR.
- Force feedback actuators are also being researched to simulate physical sensations like movement, vibration, or collision within virtual environments, enhancing the overall experience of interacting with 8K virtual worlds.
Eye Tracking and Dynamic Focusing
- Eye-tracking technology is another area of R&D in 8K VR, which can improve foveated rendering, enabling more efficient use of processing power by focusing on areas the user is looking at. This technology also supports dynamic focus adjustments based on the user’s eye movements, improving visual clarity in ultra-high-resolution environments.
- The combination of eye-tracking and pupil distance adjustment is crucial to creating a more natural and comfortable viewing experience for users, especially given the high visual fidelity of 8K VR.
5. Content Creation and Delivery
Immersive Content Creation
- The shift to 8K VR necessitates the development of new tools for immersive content creation. Researchers are developing software for creating 3D models, environments, and interactive elements at 8K resolution, which can be processed efficiently and viewed in real-time. Content creation tools will need to support high fidelity for realistic simulations in gaming, architecture, medical training, and industrial design.
- Virtual production techniques, such as motion capture and 360-degree video recording, are advancing to allow filmmakers and content creators to produce 8K VR films and interactive experiences.
Cloud Computing for VR
- Given the high data demands of 8K VR, cloud computing is a critical focus area in R&D. Cloud platforms can render 8K VR content remotely and stream it to VR headsets with minimal latency. This would allow users with less powerful local hardware to enjoy the full benefits of 8K VR.
- Companies are investing in edge computing and 5G networks to enhance the delivery of 8K VR content to users, reducing lag and enabling seamless streaming experiences even for complex, interactive VR content.
6. Ergonomics and User Comfort
Lightweight Designs and Battery Life
- One of the challenges in VR headsets, especially those with 8K resolution, is ensuring that the headset is not too heavy or uncomfortable for extended use. R&D efforts are focused on creating lightweight materials, like carbon fiber and flexible plastics, to reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity.
- Another area of focus is battery life. 8K VR headsets require substantial power, so developing high-density batteries and efficient power management systems is a priority to ensure users can engage in long sessions without constant recharging.
Reducing Motion Sickness
- With higher resolutions come increased concerns about motion sickness and visual discomfort. Research is focused on improving latency reduction, frame synchronization, and refresh rate optimization to minimize motion sickness, a common issue in VR experiences.
- Additionally, virtual reality calibration systems are being designed to ensure that each user can adjust the headset settings for optimal visual comfort and reduce the likelihood of discomfort during use.
Conclusion
The R&D efforts focused on 8K Virtual Reality (VR) headsets are broad and complex, addressing challenges in display technology, processing power, optics, user interaction, and content creation. As the technology matures, we expect significant improvements in resolution, immersion, and comfort, which will drive adoption across industries such as gaming, medical training, education, engineering, and entertainment. With innovations in cloud computing, eye-tracking, and haptic feedback, 8K VR headsets will soon become mainstream, offering ultra-realistic, immersive experiences that were once considered
Courtesy: Meta
References
- ^ Vr, Oculus. “Oculus All in on OpenXR: Deprecates Proprietary APIs”.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e f There currently exists no industry standard measurement of field of view, so numbers may be imprecise and can vary from person to person.
- ^ “The Wide5 HMD”. Archived from the original on 2007-06-28. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ “nVisor SX”. www.tekgear.com. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ “nVisor SX111”. Retrieved 2024-03-22.
- ^ “ST50”. www.tekgear.com. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ Sensics. “xSight Lightweight Panoramic HMD” (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2022-10-03. Retrieved 2022-10-02.
- ^ “Sensics HMDs”. docs.worldviz.com. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ “Sensics – Panoramic Head-Mounted Displays”. 2008-08-30. Archived from the original on 2008-08-30. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Hornyak, Tim. “Slip on this hat for a full virtual-reality experience”. CNET. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ “CrunchGear » Archive » Tokyo Virtual Reality Expo 2008: $80,000 high-end VR helmet presented”. 2008-07-01. Archived from the original on 2008-07-01. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ “HEWDD-1080(English)|ハイエンドHMD”. 2011-07-08. Archived from the original on 2011-07-08. Retrieved 2022-10-03.
- ^ HEWDD-1080 – Presentation, retrieved 2022-10-03
- ^ Peckham, Matt (6 January 2015). “Here’s the $200 Competitor Oculus Should Worry About”. Time. Archived from the original on 24 January 2015. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ Jones, Brad (2015-10-26). “Public pre-orders for Razer’s OSVR headset are now open”. www.digitaltrends.com. Retrieved 2020-09-13.
- ^ “OSVR Confirms Pre-order Date for Hacker Development Kit; Launches Content Discovery Platform – Razer Press”. Retrieved 2022-10-05.
- ^ “Razer OSVR Hacker Developer Kit 1.4 Review”. Retrieved 2019-05-07.
- ^ “Razer OSVR HDK 1.4: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Orland, Kyle (11 April 2016). “The Ars VR headset showdown—Oculus Rift vs. HTC Vive”. Ars Technica. Retrieved 6 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d “PlayStation VR is cheaper than Oculus Rift and HTC Vive”. BBC News. 15 March 2016.
- ^ Ok, Doc (1 April 2016). “Optical Properties of Current VR HMDs”. Doc-Ok.org. Retrieved 26 December 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Oculus Rift vs. Vive Pro”. 2018-04-18. Retrieved 2018-07-17.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Lang, Ben (6 April 2017). “New HTC Vives Weigh 15% Less Than They Did at Launch”. Road to VR. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “Oculus Rift: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Robertson, Adi (March 20, 2019). “The Oculus Rift is out of stock almost everywhere, still shipping ‘while supplies last'”. The Verge. Vox Media, Inc. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
While we don’t comment on specific shipment windows or allocations, [we] can confirm [the] original Rift is still available for sale at Oculus.com and from our retail partners while supplies last.
- ^ “HTC Vive Teardown”. IFixit. 26 April 2016. Retrieved 11 October 2019.
- ^ “HTC Vive: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ “Vive | Product”. www.htcvive.com. Retrieved 2018-04-02.
- ^ Summers, Nick (13 June 2016). “OSVR improves the display on its new developer headset”. Engadget. Archived from the original on 13 June 2016. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ Matney, Lucas (20 July 2016). “Razer opens pre-orders for OSVR HDK 2 virtual reality headset”. TechCrunch. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Razer | OSVR Hacker Dev Kit”. Razer. Archived from the original on 2015-07-18. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
- ^ “Razer OSVR HDK 2: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Starbreeze News Archive (2016-08-31). “Acer and Starbreeze Announce First Shipment of StarVR Head-Mounted Displays – Starbreeze”. Starbreeze. Retrieved 2020-09-13.
- ^ “Starbreeze’s spec heavy StarVR headset is now shipping to IMAX VR centres”. Wareable. Retrieved 2017-06-26.
- ^ “HTC Vive vs StarVR| Comparison virtual reality specifications”. all-smart.eu. Retrieved 2017-06-26.
- ^ “Tips and Specs – PlayStation Virtual Reality Headset”. PlayStation.com. Sony Interactive Entertainment LLC. Retrieved 7 October 2019.
- ^ Lang, Ben (2015-09-17). “Sony Confirms New 90Hz Display Mode for PlayStation VR”. Road to VR. Retrieved 2019-05-03.
- ^ Griffiths, Brendan (1 October 2019). “The best cheap PlayStation VR bundles, prices and deals in October 2019”. Techradar. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ Brown, Mike (23 November 2018). “Why You’ll Want to Buy the Move Controllers for PlayStation VR”. Inverse. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ Rubin, Peter (19 April 2019). “Exclusive: What to Expect From Sony’s Next-Gen PlayStation”. Wired. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c d e Peñaflorida, Rexly (16 September 2016). “‘FOVE 0’ VR HMD Hardware, Minimum System Specs Finalized”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ Feltham, Jamie (20 January 2017). “Eye-Tracking VR Headset FOVE 0 Costs $599, Starts Shipping (Update)”. UploadVR. UVR Media LLC. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ Stein, Scott (4 January 2017). “Fove 0’s eye-tracking VR is here, and it points to the future (hands-on)”. CNET. Retrieved 3 October 2019.
- ^ Zelenika, Kresimir (2016-11-10). “Hands On Review: PIMAX 4K VR Headset”. VR World. Archived from the original on 10 November 2016. Retrieved 2017-06-20.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c Pirzada, Usman (9 June 2017). “The PIMAX 4K VR Headset Hands On Review: Affordable PC VR For The Masses At $375?”. WCCFTech. Retrieved 11 October 2019.
- ^ “Pimax 4K: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Jagneaux, David (19 July 2017). “Hands-On: The VRHero Is A 5K Resolution Headset From VRgineers”. UploadVR. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ “Technical Specifications |”. VRGineers.com. Archived from the original on 27 July 2017. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ “VRgineers VRHero 5K: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Timo (6 June 2017). “DeePoon E3 – Virtual Reality 3D glasses Quelle”. Techreviewer. Retrieved 8 October 2019.
- ^ VR, Deepoon. “China’s DPVR Launches New PC Helmet E3”. www.prnewswire.com (Press release). Retrieved 2017-06-26.
- ^ Bruce, James (7 November 2017). “Dell Visor Mixed Reality Headset Review [Updated]”. MakeUseOf. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ “Dell Visor Shipping Globally Tomorrow, October 17”. VR and Fun. 16 October 2017. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ “Dell Visor: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Smith, Sherri (20 October 2017). “Acer Mixed Reality Headset Review: It’s Empty in Here”. Tom’s Guide. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Comparing Windows Mixed Reality headsets from Acer, ASUS, Dell, HP, Lenovo and Samsung”. 2017-09-13. Retrieved 2018-07-17.
- ^ Lacort, Javier (2017-08-31). “Lenovo Explorer, la realidad mixta de Windows empieza a florecer” (in Spanish). Retrieved 2017-09-01.
- ^ “Samsung Odyssey Windows VR Headset Now Available – Everything You Need to Know”. Virtual Reality Pulse. Retrieved 2017-11-25.
- ^ Lang, Ben (1 February 2018). “Hands-on: VRHero “5K” Plus Aims for Visual Fidelity Above All Else”. Road to VR. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ “VRHero 5K (Plus) Technical Specifications”. VRgineers.com. Archived from the original on 29 December 2017. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ “VRHero 5K Plus: The world’s first VR headset with high-density OLED displays—topping those of the new iPhone X—delivering unparalleled image quality in virtual reality” (PDF). VRgineers.com. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ Carbotte, Kevin (12 June 2018). “Asus Windows Mixed Reality Headset Review: Nice, But High-Priced”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ “Asus Windows VR Headset Finally Launches, Priced at $430”. 2018-02-20. Retrieved 2018-07-17.
- ^ “Asus HC102: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Orland, Kyle; Machkovech, Sam (4 March 2018). “HTC Vive Pro review: Eye-popping VR, with a price that’s a little too real”. Ars Technica. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “OLED-info HTC Vive Pro”. www.oled-info.com. Retrieved 2019-05-30.
- ^ “Vive Pro Product Description”. Retrieved 2019-05-13.
- ^ “Review: HTC Vive Pro”. Focus on VR. 24 December 2018. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “HTC Vive Pro: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Lang, Ben (26 June 2018). “VRgineers Reveals Improved ‘XTAL’ Professional Headset with Auto IPD Adjustment & Leap Motion”. Road to VR. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ “VRgineers Unveils XTAL, a New Smart Headset for Professionals Packed with Novel Technology”. VRgineers.com. 26 June 2018. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “XTAL Technical Specification”. VRgineers.com. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ Osborne, Joe (14 August 2018). “StarVR One is the most powerful VR headset yet, and you can’t have one”. Techradar. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ^ Hamilton, Ian (14 August 2018). “StarVR One: 90 FPS, SteamVR Tracking 2.0 With ‘Nearly’ Human FoV”. UploadVR. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ^ “StarVR – Developer Program”. StarVR.com. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ^ “Samsung’s Odyssey+ Costs $500, Uses Anti-Screen Door Effect Display”. Retrieved 2019-07-11.
- ^ “Samsung Odyssey+: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Carbotte, Kevin (2 March 2019). “Pimax 5K Plus Review: A Fresh Look at Ultrawide VR”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ Hayden, Scott (30 November 2018). “Pimax Announces General Sale of “8K” & “5K” Headsets with 80+ Day Waiting Period”. Road to VR. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ Bruce, James (12 September 2019). “Pimax 5K Plus Ultrawide VR Headset Offers a Glimpse Into the Future”. MakeUseOf. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “VRgineers Reveals Improved ‘XTAL’ Professional Headset with Wider FOV”. Road to VR. 11 December 2018. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ “XTAL Technical Specification”. VRgineers.com. Archived from the original on 30 June 2019. Retrieved 20 October 2019.
- ^ Lang, Ben (19 February 2019). “Varjo Launches VR-1 with Retina-quality Fixed-foveated Display & Eye-tracking, Priced at $6,000”. Road to VR. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ “Varjo VR-1: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ “Varjo Aero”. Varjo.com. Retrieved 2022-07-27.
- ^ “Varjo Aero Headset Brings Highest-Fidelity VR For Leading-Edge Users”. Varjo.com. 2021-10-21. Retrieved 2022-07-27.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “GDC 2017: Hands-on With LG’s SteamVR Headset”. UploadVR. 2017-03-01. Retrieved 2017-06-20.
- ^ “Pimax 8K Series”. Pimaxvr.com. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Pimax8K”. Pimax Technology. Retrieved 2019-05-01.
- ^ “Pimax 8K VR Headset”. Niora.net. Retrieved 2020-05-30.
- ^ Carbotte, Kevin (9 August 2019). “Valve Index VR Headset and Controllers Review: First Benchmarks”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 17 October 2019.
- ^ Dingman, Hayden (28 June 2019). “Valve Index review: The new bar for VR headsets”. PC World. IDG Communications, Inc. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- ^ Lang, Ben (1 May 2019). “Index’s ‘Off-ear’ Headphones Are Its Most Surprising Innovation”. Road to VR. Retrieved 17 October 2019.
- ^ Machkovech, Sam (2019-04-30). “Valve Index reveal: The best of VR’s first generation—but is it worth $999?”. Ars Technica. Retrieved 2019-05-02.
- ^ “HP Reverb VR Headset Hands-On: HTC Vive Pro’s Got Competition”. Tom’s Hardware. 2019-03-19. Retrieved 2019-03-19.
- ^ Goode, Lauren (2019-03-19). “HP’s New Reverb VR Headset Bumps Up the Resolution”. Wired. ISSN 1059-1028. Retrieved 2019-03-19.
- ^ “HP Reverb VR Headset might’ve hit the sweet spot”. SlashGear. 2019-03-19. Retrieved 2019-03-19.
- ^ Lang, Ben (2019-07-30). “HP Reverb Still ‘Sold Out’ as Reports of Display Issues Continue”. Road to VR. Retrieved 2020-09-13.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Carbotte, Kevin (15 May 2019). “HP Reverb VR Headset Review: Windows Mixed Reality Never Looked So Good”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “HP Reverb: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Statt, Nick (2019-03-20). “Oculus unveils the Rift S, a higher-resolution VR headset with built-in tracking”. The Verge. Retrieved 2019-03-21.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Carbotte, Kevin (30 June 2019). “Oculus Rift S Review: First-Gen VR Gets a Reboot”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 7 October 2019.
- ^ “Is Samsung’s HMD Odyssey+ better than Oculus Rift S?”. Windows Central. 2020-06-24. Retrieved 2021-04-15.
- ^ “Oculus Rift S: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Shilov, Anton (2019-09-13). “HTC Unveils Final Specs & Availability Date of Cosmos VR Headset for PCs”. AnandTech. Retrieved 2019-09-30.
- ^ Carbotte, Kevin (3 October 2019). “HTC Vive Cosmos VR Headset Review: Solid Upgrade”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 4 October 2019.
- ^ “HTC Vive Cosmos: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Lang, Ben (15 October 2019). “Varjo Launches VR-2 Headset with SteamVR Support, Improved ‘Bionic Display’, and Hand-tracking Option”. Road to VR. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ “Introducing Varjo VR-2”. Varjo.com. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ “Varjo VR-2: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Play Rift Content on Quest with Oculus Link, Available Now in Beta!”. Oculus.com. 18 November 2019. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ^ Jump up to:a b Rakver, Martin. “Oculus Quest 2 FOV & Comparison With Other Headsets”. Smart Glasses Hub. Retrieved 2021-04-15.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Oculus Quest: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Introducing Oculus Air Link, a Wireless Way to Play PC VR Games on Oculus Quest 2, Plus Infinite Office Updates, Support for 120 Hz on Quest 2, and More”. www.oculus.com. Retrieved 2021-04-24.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Oculus Quest 2: Full Specification”. VRcompare. 24 March 2021. Retrieved 24 March 2021.
- ^ “Latest Update on the HP Reverb G2 Virtual Reality Headset”. press.hp.com. Retrieved 2020-11-23.
- ^ Lang, Ben (8 September 2021). “Varjo VR-3 Has Industry-Leading Resolution, XR-3 Model Gets LiDAR”. UploadVR. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- ^ “PlayStation VR2 and PlayStation VR2 Sense controller: the next generation of VR gaming on PS5”. January 4, 2021. Archived from the original on 2022-01-05.
- ^ “PlayStation VR2 launches in February at $549.99”. PlayStation.Blog. November 2, 2022.
- ^ Abent, Eric (2016-10-12). “Nolan Bushnell Launches Modal VR, A Virtual Reality System Aimed At Enterprise”. SlashGear.com. Retrieved 2022-10-10.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Gear VR for Galaxy Note5, Galaxy S6 edge+, Galaxy S6 edge, and Galaxy S6”. Samsung Electronics America. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
- ^ “The best VR headsets”. Wareable. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Avegant Glyph | Product”. www.avegant.com. Archived from the original on 2016-04-07. Retrieved 2016-04-02.
- ^ “Pico Interactive | VR for all – instant, easy and ultra portable”. Pico Interactive. Retrieved 2017-07-31.
- ^ “The standalone Pico Goblin VR headset will arrive this summer for $249”. Wareable. Retrieved 2017-07-31.
- ^ “Pico Goblin: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ “A new era in virtual reality with the Snapdragon VR820 reference platform | Qualcomm”. Qualcomm. 2016-09-01. Retrieved 2017-03-02.
- ^ “The Pico Neo CV Is A Fully Untethered, Positionally Tracked VR Headset”. UploadVR. 2017-01-05. Retrieved 2017-03-02.
- ^ “Pico Neo CV: This is virtually freedom”. Wareable. Retrieved 2017-03-02.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “A Guide to Pico Neo VR Headsets”. Program-Ace. Retrieved 2021-12-29.
- ^ “Qualcomm Introduces Snapdragon 835 Virtual Reality Development Kit | Qualcomm”. Qualcomm. 2017-02-23. Retrieved 2017-03-02.
- ^ “Woxter Neo VR100 el nuevo concepto de gafas VR de Woxter”. VirtualWorld, Realidad Virtual, Mixta y Aumentada (in European Spanish). 2017-01-05. Archived from the original on 2017-12-01. Retrieved 2017-11-25.
- ^ “Woxter Neo VR100: Full Specification”. VRcompare.
- ^ “HTC reveals standalone Vive Focus VR headset and cancels Daydream plans”. The Verge. Retrieved 2017-11-25.
- ^ “HTC’s Vive Focus is the company’s new standalone VR headset”. 2017-11-13. Retrieved 2018-07-17.
- ^ “Oculus Go, el standalone de 199 dólares compatible con Gear VR”. www.realovirtual.com (in Spanish). Retrieved 2017-10-11.
- ^ Harding, Scharon (20 December 2018). “What Is FOV? A Basic Definition”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- ^ Green, Sam (6 September 2018). “Oculus Go Review”. VR Geeks. Retrieved 2 October 2019.
- ^ “HTC Vive and Lenovo are developing standalone Daydream VR headsets”. Engadget. Retrieved 2017-11-25.
- ^ Carbotte, Kevin (24 May 2018). “Nvidia’s Jetson TX2 Powers GameFace Labs’ Standalone VR Headset”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ “Features | GameFace Labs”. GameFace Labs. Retrieved 13 October 2019.
- ^ “WhatVR Headset Comparison Table”. WhatVR. Retrieved 2018-07-23.
- ^ Protalinski, Emil (15 October 2019). “Google discontinues Daydream VR”. VentureBeat. Retrieved 16 October 2019.
- ^ “Hands-on With ‘Santa Cruz’ Inside Out Position Tracking Oculus Prototype – UploadVR”. UploadVR. 2016-10-06. Retrieved 2017-07-05.
- ^ “With the cord-free Quest, Oculus finally makes high-quality VR easy”. Digital Trends. 2018-09-27. Retrieved 2018-10-02.
- ^ “GDC 2018: Oculus Go And Santa Cruz Have 72Hz Modes”. UploadVR. 2018-03-21. Retrieved 2018-03-23.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Oculus Quest 2 Review: The New King Of VR”. UploadVR. 2020-10-13. Retrieved 2020-10-18.
- ^ Jump up to:a b c “Review: Facebook’s Oculus Quest 2 is outstanding”. TechCrunch. Retrieved 2020-10-18.
- ^ Kevin Carbotte (2021-06-28). “HTC Vive Focus 3 Review: Standalone VR Done Right”. Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved 2023-03-07.
- ^ “Pico Neo 3 Pro | VR Expert | VR&AR | Hardware & Service”. VR Expert | Enterprise VR/AR Hardware Supplier. 12 February 2020. Retrieved 2021-12-29.
- ^ “VIVE Flow Specs | VIVE United States”. www.vive.com. Retrieved 2022-03-11.
- ^ “HTC’s Vive Flow Is Light in Weight but Not Features”. Lifewire. Retrieved 2022-03-11.
- ^ Cureton, Demond (2022-10-19). “ThinkReality VRX Hits ‘High Marks,’ Lenovo Exec Says”. XR Today. Retrieved 2023-04-27.
- ^ “It’s all in the details”. 2022-11-01.
- ^ Lang, Ben (2022-10-11). “Quest Pro Specs & Features Revealed: Pre-orders Available Today, Shipping October 25th for $1,500”. Road to VR. Retrieved 2023-03-07.
- ^ “Bigscreen”. bigscreenvr.com. Retrieved 2024-03-24.
- ^ Hayden, Scott (2023-09-08). “Thin & Light Bigscreen Beyond Now Shipping in US, International Shipments Coming Soon”. Road to VR. Retrieved 2024-03-24.
- ^ “Apple Reportedly Can’t Make Many Vision Pro Headsets”. UploadVR. 2023-06-13. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Vision Pro Teardown Part 2 – Is the Apple Vision Pro Really 4K?”. Youtube. 2024-02-07. Retrieved 2024-02-12.
- ^ “r/oculus – What happened to the LG SteamVR headset?”. reddit. 27 April 2018. Retrieved 2019-04-28.
- ^ devindra (17 May 2017). “HTC Vive and Lenovo are developing standalone Daydream VR headsets”. Engadget. Retrieved 2017-07-27.
- ^ “VIVE | New HTC VIVE standalone VR headset with Google Daydream. No phone or PC required”. www.vive.com. Archived from the original on 2017-07-18. Retrieved 2017-07-27.
- ^ Roettgers, Janko (14 November 2017). “HTC Cancels Google Daydream Standalone VR Headset”. Variety. Retrieved 21 October 2019.
- ^ Twitter https://twitter.com/decagear/status/1441427033645404168. Retrieved 2021-09-26.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ “Oculus Rift CV1 Teardown”. iFixit. 30 March 2016. Retrieved 2016-04-09.
- ^ “Asynchronous Timewarp Examined”. developer.oculus.com. Retrieved 2016-02-23.
- ^ “SteamVR Developer Hardware: Interleaved Reprojection now enabled for all applications by default”. steamcommunity.com. Retrieved 2016-03-29.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “StressLevelZero on Twitch stream confirms fov as around 80h90v • /r/oculus”. reddit. 29 March 2016. Retrieved 2016-03-29.
- ^ Buckley, Sean (19 May 2015). “This Is How Valve’s Amazing Lighthouse Tracking Technology Works”. Gizmodo. Retrieved 2016-02-23.
- ^ “Oculus Touch Controllers Are A Lighter and Better Touch Than HTC Vive | Tom’s Guide”. www.tomsguide.com. 26 September 2018. Retrieved 2020-08-21.
- ^ “Steam Community :: Group Announcements :: SteamVR”. steamcommunity.com. 23 March 2016. Retrieved 2016-03-25.
- ^ “SteamVR Plugin – Asset Store”. www.assetstore.unity3d.com. Archived from the original on 2015-06-18. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ^ Jump up to:a b “Virtual Reality technology is evolving rapidly and becoming more powerful and immersive by the day. Even if you’re starting with a simple project to learn VR or AR, build your team, your assets and your workflow around a technology that can deliver on your creative vision – now and in the future”. www.unrealengine.com. Archived from the original on 2015-06-29. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ^ “CRYENGINE V – CRYENGINE Home – Documentation”. docs.cryengine.com. Archived from the original on 2016-03-18. Retrieved 2016-03-16.
- ^ Engine, Godot. “Godot Engine – Update on recent VR developments”. godotengine.org. Retrieved 2018-12-21.
- ^ Technologies, Unity. “Unity – Manual: Oculus”. docs.unity3d.com. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ^ “VR – Oculus Rift – Technical Documentation – Documentation”. docs.cryengine.com. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ^ “Godot Engine – Godot Oculus Quest support”. godotengine.org. Retrieved 2020-08-27.
- ^ “Microsoft Mixed Reality”. Unity. Retrieved 2019-05-09.
- ^ “OSVR Plugin – Asset Store”. www.assetstore.unity3d.com. Archived from the original on 2015-06-18. Retrieved 2016-02-24.
- ^ “Native OSVR support comes to Unreal game engine”. TechCrunch. Retrieved 2019-04-19.
- ^ “VR – OSVR – CRYENGINE Programming – Documentation”. docs.cryengine.com. Retrieved 2019-04-19.